In this article, we convey how to use the “find” command to search files efficiently either through some expressions or patterns in an Ubuntu machine. If you are a new user of Linux, then you can master it by learning various conditions of the “find” command.
Find Command Syntax:
Where directory-path contains the complete path of a directory, filename contains the name of a file which you want to search, whereas you have several options such as move, copy, delete.
1. Find file through Name
It is one of the easiest commands which assists you to find a specific file by name within a directory. By using this command, you can easily find all the files having the same name within the passed directory path if it is present in one of the folders.
Syntax:
Where name option is case-sensitive.
Example
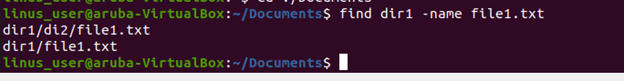
In this example, we are going to find a file recursively such as “file1.txt” within the folder “dir1”.
If you want to find a file by name which is not case-sensitive, you can enter the filename either in uppercase or lowercase. You can find files irrespective of the case by simply replacing the option “name” with “iname”.
Syntax
Example:
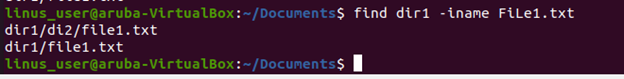
In this example, we are going to find a file named “file1.txt” within the folder “dir1” but we entered the characters of the filename in upper and lower case.
2. Finding a file through expression statement
You can also find files from the directory by using regular expressions. In this command, “-regex” tells us that we are going to pass a regular expression, then “.” match up no. of characters within the file. Subsequently, “*” matches the repetition of characters. At the last, you are going to pass the file extension.
Syntax
Example
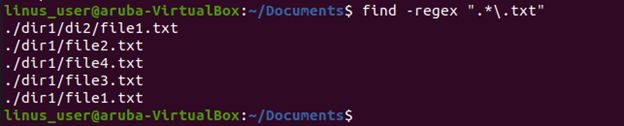
In this example, we are going to find all files which have an extension of ‘.txt’ at the end.
Find files by the regular expression is good as it allows you to search files with multiple extensions at once.
Syntax
Example
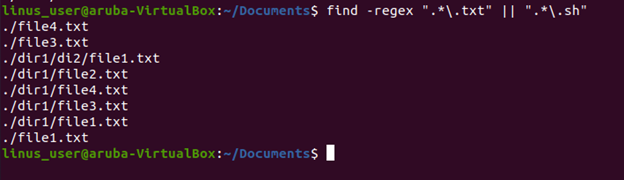
In this example, we going to find all the files which have an extension of .txt and .sh.
3. Find modified files through n minutes
You can also search modified files within the last n minutes.
Syntax
Where N represents minutes
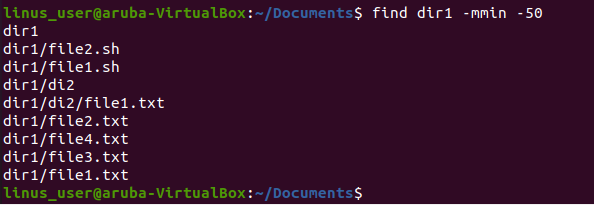
Example
In this example, we find all the files that are modified 50 minutes back.
4. Find files that are empty
You can also find all empty directories within the entered directory.
Syntax
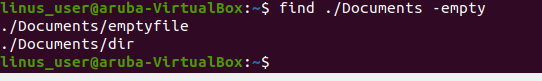
Example
In this example, we find empty folders reside in the documents folder.
5. Find modified files through n days
By using the “find” command, you can easily search modified files within the N no. of days.
Syntax:
Where n represents the last modified days.
Example
The below-mentioned command finds all the files that are modified within a day.
6. Find files by entering specific permissions
You can also find files with specific entered permissions.
Syntax
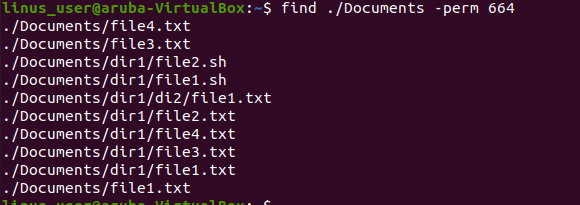
Example
In this example, we are going to find files within the Documents folder and subfolders with 644 permission. 644 permission means that only the host who creates the file has the authority to read or write.
$
You can also find all files which are connected to a user.
Syntax
Example
7. Find files by specifying the size
You can also find files which are smaller or greater than the entered size.
Syntax: Find files bigger than n size
Where n is the size of the file, “+” operator is used to search files greater than n size of the file.
Syntax: Find files smaller than n size
Where n is the size of the file, “-” operator is used to search files smaller than n size of the file.
There are various options of bytes like M is used for Megabytes. Similarly, G is used for Gigabytes, k is used for kilobytes.
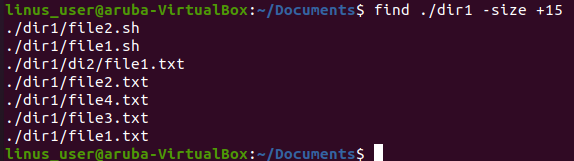
Example
In this example, we are going to find files from the folder of dir1 whose size is greater than 15. Byte block is the default unit if you cannot specify any option next to the size of the file as shown in the picture below.
In this example, we are going to find files from the folder of dir1 whose size is smaller than 10 megabytes.
8. Find files by specifying the type
You can also find files by specifying the type of file. The “find” command has various types like “f” is used to find files, “d” is used to find directories, etc.
Syntax
Example
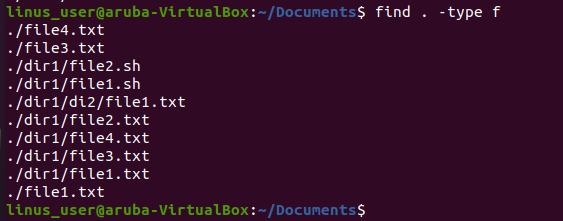
In this example, we are going to find directories that reside in the Document folder.
Then we are going to find all the files that reside in the document folder as well as in sub-folders.
9. Find files by using multiple conditions
You can also find files by combining different conditions by using a single command. In this example, we are going to find files whose size is greater than 1 kilobyte and also have an extension of .txt.
Conclusion
This article clearly demonstrates the effectiveness and efficiency of the “find” command to find the located files through name, permission or type, etc. Examples are also provided which helps you understand the better usage of each find command.