This tutorial will walk you through exporting a database schema without including all the records.
Creating Sample Database and Records
Before illustrating how to export databases and schema, let us create a database, tables, and records.
Feel free to use the source code provided in the snippet below or your database schema.
use linuxhintdb;
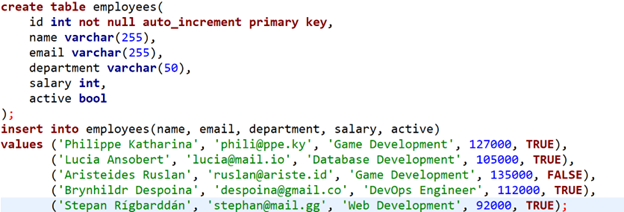
Once we have created and connected to the database, we can create a sample table and add data as shown in the query below:
id int not null auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(255),
email varchar(255),
department varchar(50),
salary int,
active bool
);
insert into employees(name, email, department, salary, active)
values ('Philippe Katharina', '[email protected]', 'Game Development', 127000, TRUE),
('Lucia Ansobert', '[email protected]', 'Database Development', 105000, TRUE),
('Aristeides Ruslan', '[email protected]', 'Game Development', 135000, FALSE),
('Brynhildr Despoina', '[email protected]', 'DevOps Engineer', 112000, TRUE),
('Stepan Rígbarddán', '[email protected]', 'Web Development', 92000, TRUE);
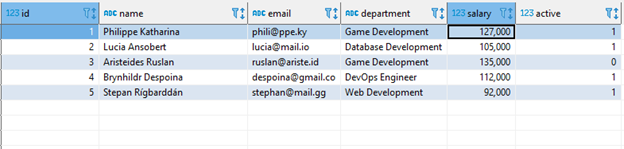
We can verify the data using the select statement:
Output table:
MySQL Export Database Without Data
Once we have the sample database and records ready, we can proceed and discuss how to export database schema.
Using MySQLDump
One of the most valuable tools in the MySQL arsenal is the MySQLDump utility. It allows you to dump a database and all the records in it. This is very useful when performing backups.
We can use this tool to export the database’s structure/schema as shown in the command below:
For example, to export linuxhintdb schema:
The command above should create an XML file containing the schema of the specified database. An example XML output is as shown:
<mysqldump xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<database name="linuxhintdb">
<table_structure name="employees">
<field Field="id" Type="int" Null="NO" Key="PRI" Extra="auto_increment" Comment="" />
<field Field="name" Type="varchar(255)" Null="YES" Key="" Extra="" Comment="" />
<field Field="email" Type="varchar(255)" Null="YES" Key="" Extra="" Comment="" />
<field Field="department" Type="varchar(50)" Null="YES" Key="" Extra="" Comment="" />
<field Field="salary" Type="int" Null="YES" Key="" Extra="" Comment="" />
<field Field="active" Type="tinyint(1)" Null="YES" Key="" Extra="" Comment="" />
<key Table="employees" Non_unique="0" Key_name="PRIMARY" Seq_in_index="1" Column_name="id" Collation="A" Cardinality="5" Null="" Index_type="BTREE" Comment="" Index_comment="" Visible="YES" />
<options Name="employees" Engine="InnoDB" Version="10" Row_format="Dynamic" Rows="5" Avg_row_length="3276" Data_length="16384" Max_data_length="0" Index_length="0" Data_free="0" Auto_increment="6" Create_time="2022-08-09 13:58:22" Update_time="2022-08-09 13:58:30" Collation="utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci" Create_options="" Comment="" />
</table_structure>
</database>
</mysqldump>
If you are looking for an extended version of the command, we can use the command:
In this case, the command tells the MySQLDump utility to skip lock tables, add drop commands, and add extended-insert.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to export a database schema without including the data using the MySQLDump utility.