This blog will explain the procedure to return a boolean method in Java.
How to Return a Boolean Method in Java?
As we discussed earlier, the return type of method is mentioned in the method declaration. If a method is declared with a boolean return type, it gives a boolean value.
Syntax
Follow the syntax for returning a boolean method in Java.
return false;
}
Here, “abc()” is a boolean method that returns the boolean value “false”.
Now, let’s head toward the implementation of the Boolean method in Java.
Example 1: Implementing a Simple Boolean Method
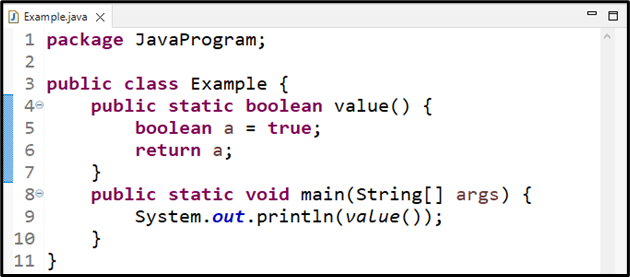
We will create a boolean method named “value()” that contains a boolean variable “a” with the value “true”. The return statement of this method will be a boolean as the method is declared as a boolean type:
boolean a = true;
return a;
}
We will call the boolean method value() in the main() method to print out the returned value:
System.out.println(value());
}
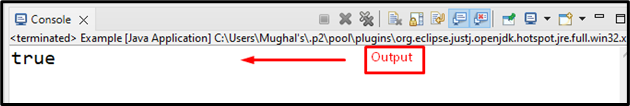
The output displayed the “true” as the returned value:
Let’s see how the boolean method works with conditional statements.
Example 2: Adding if-else Conditional Statement in Boolean Method
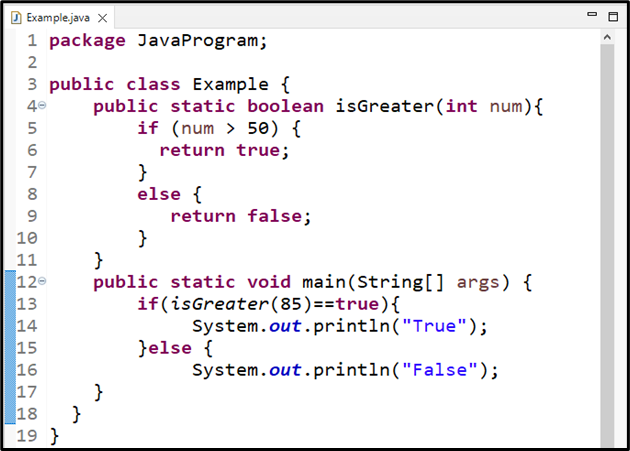
Here, we will create a boolean method named “isGreater()” with an integer type parameter “num”. If num is greater than “50”, the method will return “true” else “false”:
if (num > 50) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
We will call the isGreater() method by passing a number “85” in main() method, and check if the returned value is equals to true, then it will print “True”, else display “False”:
if(isGreater(85)==true){
System.out.println("True");
}else {
System.out.println("False");
}
Output
Look at one more example to understand the concept.
Example 3: Checking If a Number is Odd or Even Using Boolean Method
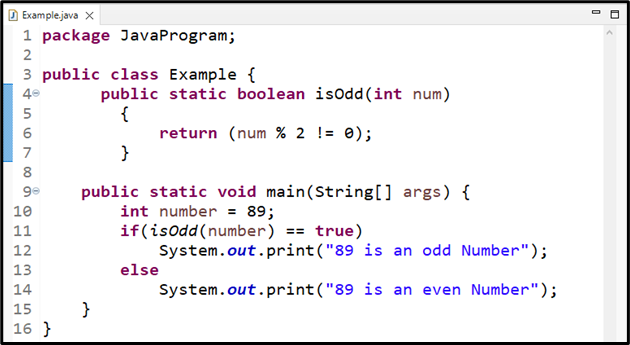
First, we will create a boolean method named “isOdd()” that returns the boolean value true or false. The statement “return (num % 2 != 0)” will return true, if the result is not equals to 0, otherwise it returns false:
{
return (num % 2 != 0);
}
Now, in the main() method, we will create an integer type variable named “number” assigned with value “89”. The “isOdd()” method will accept the created integer as an argument. The given method will print out the specified statements according to the evaluation of the given condition:
int number = 89;
if(isOdd(number) == true){
System.out.print("89 is an odd Number");
}else{
System.out.print("89 is an even Number");}
}
The output shows “True” as the isOdd() method returned true:
We gathered all the instructions to return a boolean method in Java.
Conclusion
In Java, you must declare a method of the boolean type in order for it to return a boolean value. The boolean method will return the boolean value, true or false. You can either return the variable containing a boolean value or use conditional statements to decide the returned value. In this blog, we explained the procedure to return a boolean method in Java with detailed examples.