The COUNT function counts the number of rows (entries) from a selected statement passed to the function as an input expression. It would be much harder to count the number of rows if they are hundreds or thousands.
In this blog, we will discuss how the COUNT function in Redshift can be used in different scenarios to count the number of rows.
Syntax of COUNT Function
The syntax to use the Redshift COUNT function is as follows.
COUNT ( [ DISTINCT | ALL ] * | expression )
Here, we will discuss different parameters which can be passed to the COUNT function while counting the number of rows.
DISTINCT | ALL
The DISTINCT parameter is used when you only need the count of distinct rows and remove the duplicate number of rows while counting. The ALL parameter is used when you need to count all the rows, including the duplications.
Expression
This parameter is the targeted column in the table for which you want to use the COUNT function. The COUNT function will get the input from the expression and return the number of rows. In order to count all the rows of a column in the Redshift table, you can use the (*) expression.
Examples of COUNT Function
In this section, we will see how we can apply the COUNT function in different scenarios. We can use the COUNT function in multiple ways to get the number of rows. Some of the use cases of the COUNT function are listed below:
- COUNT function on non-NULL rows
- COUNT function NULL rows
- COUNT function on multi-NULL rows
- COUNT function using (*) Parameter
- COUNT function using DISTINCT parameter
- COUNT function on NULL rows using DISTINCT parameter
COUNT Function on Non-NULL Rows
Now, we will use the COUNT function on a table where the rows have some values (NOT NULL). Let us have a table (redshift_count_function) with three columns (ID, first_name and last_name), as shown below. Now, we will apply the COUNT function on the following table to get the number of rows:
| ID | first_name | last_name |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | Dwayne | Johnson |
| 11 | Vin | Diesel |
| 22 | Will | Smith |
| 33 | Robert | Downey Jr. |
| 44 | Chris | Hemsworth |
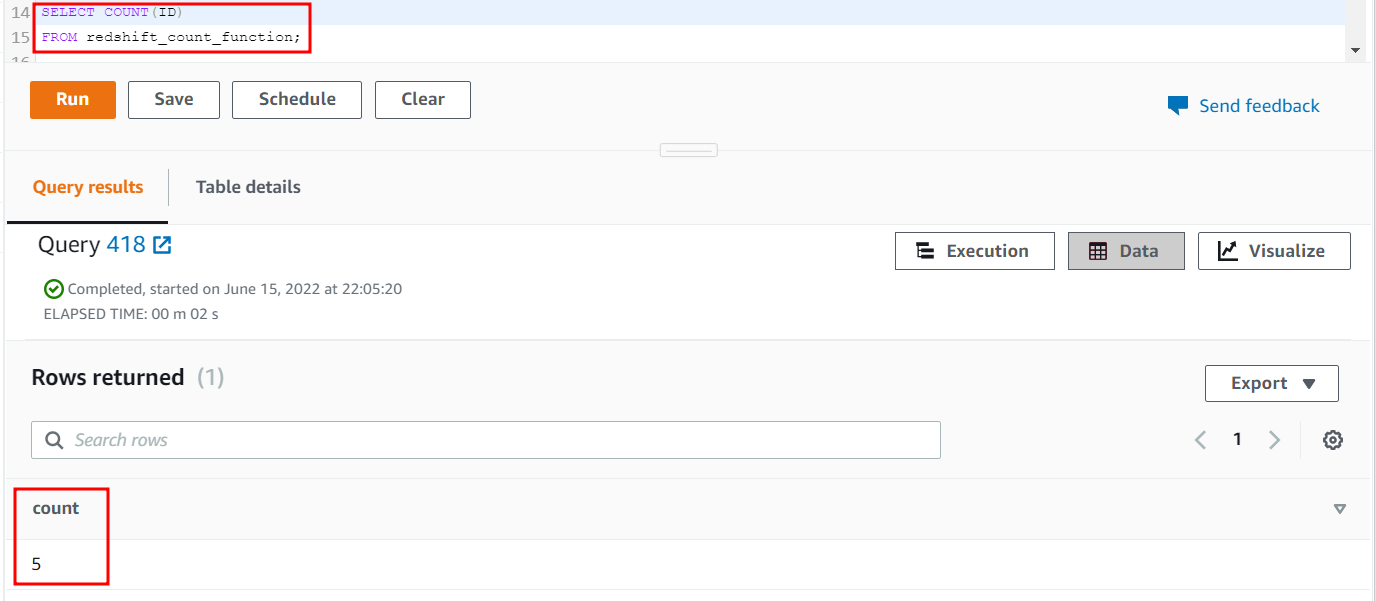
Apply the COUNT function on the ID column of the redshift_count_function table.
FROM redshift_count_function;
The output of the previous query will be as follows when executed:
5
COUNT Function on NULL Rows
The COUNT function can also be applied to count the number of entries (rows) returned by an expression. If any of the entries returned by the expression is NULL, the COUNT function will not count and exclude it from the result. In this example, we will apply the COUNT function on the column having at least one NULL value.
| S_no | first_name | last_name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dwayne | Johnson |
| 2 | Vin | Diesel |
| 3 | Will | Smith |
| 4 | Robert | Downey Jr. |
| 5 | Chris | NULL |
| 6 | Leonardo | DiCaprio |
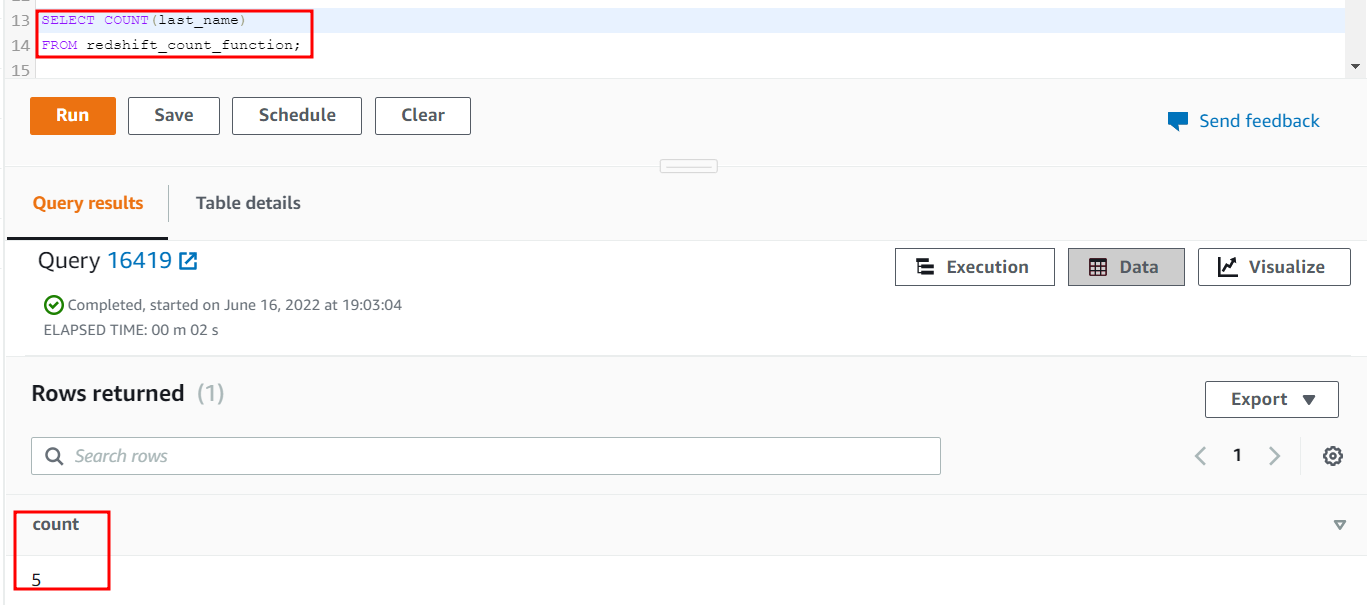
Apply the COUNT function on the last_name column of the redshift_count_function table. One row has a NULL value, so the COUNT function does not count that row.
FROM redshift_count_function;
The output of the previous query will be as follows when executed:
5
The output shows that the COUNT function only counts the rows having some values and discards the NULL row.
COUNT Function on Multi NULL Rows
Now, we have a table in which a column first_name includes multiple NULL values. Here, we will apply the COUNT function on the first_name column of the redshift_count_function table to get the number of rows which does not have a NULL value.
| S_no | first_name | last_name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dwayne | Johnson |
| 2 | NULL | Diesel |
| 3 | Will | Smith |
| 4 | NULL | Downey Jr. |
| 5 | Chris | NULL |
| 6 | NULL | DiCaprio |
Apply the COUNT function on the first_name column of the redshift_count_function table using the following query. Three rows have a NULL value so the COUNT function does not count those rows.
FROM redshift_count_function;
The output of the previous query will be as follows when executed:
3
COUNT Function Using (*) Parameter
In this example, we will apply the count function using the (*) parameter. This parameter is used when you need to count all rows, even if rows contain NULL values.
| S_no | first_name | last_name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dwayne | Johnson |
| 2 | Vin | Diesel |
| 3 | Will | Smith |
| 4 | Robert | Downey Jr. |
| 5 | Chris | NULL |
| 6 | Leonardo | DiCaprio |
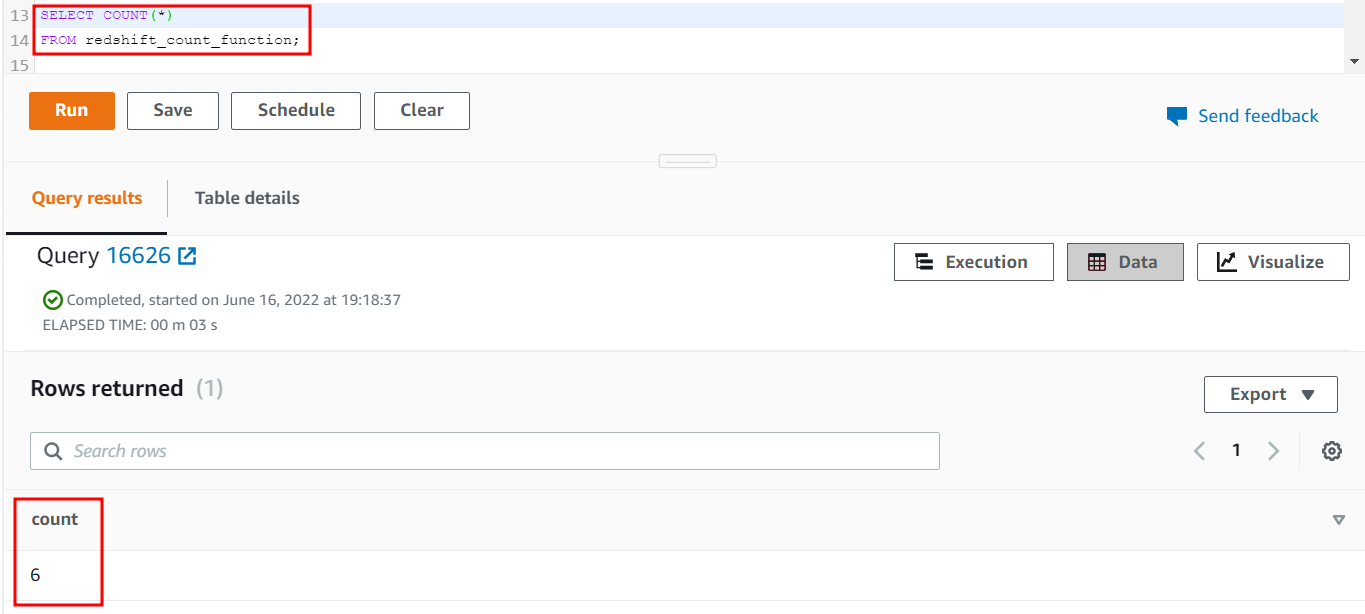
Apply the COUNT function on the redshift_count_function table by executing the following query:
FROM redshift_count_function;
The output of the previous query will be as follows when executed:
6
This example shows that the (*) parameter counts all the rows even if any row contains NULL values.
COUNT Function Using DISTINCT Parameter
In this example, we will use the COUNT function by applying the DISTINCT parameter. This parameter only counts a distinct number of rows and leaves duplicate rows.
| S_no | ID | first_name | last_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11 | Dwayne | Johnson |
| 2 | 22 | Vin | Diesel |
| 3 | 33 | Will | Smith |
| 4 | 44 | Robert | Downey Jr. |
| 5 | 55 | Chris | Hemsworth |
| 6 | 66 | Leonardo | DiCaprio |
| 7 | 77 | Dwayne | Johnson |
| 8 | 88 | Vin | Diesel |
| 9 | 99 | Will | Smith |
| 10 | 1010 | Robert | Downey Jr. |
| 11 | 1111 | Chris | Hemsworth |
| 12 | 1212 | Leonardo | DiCaprio |
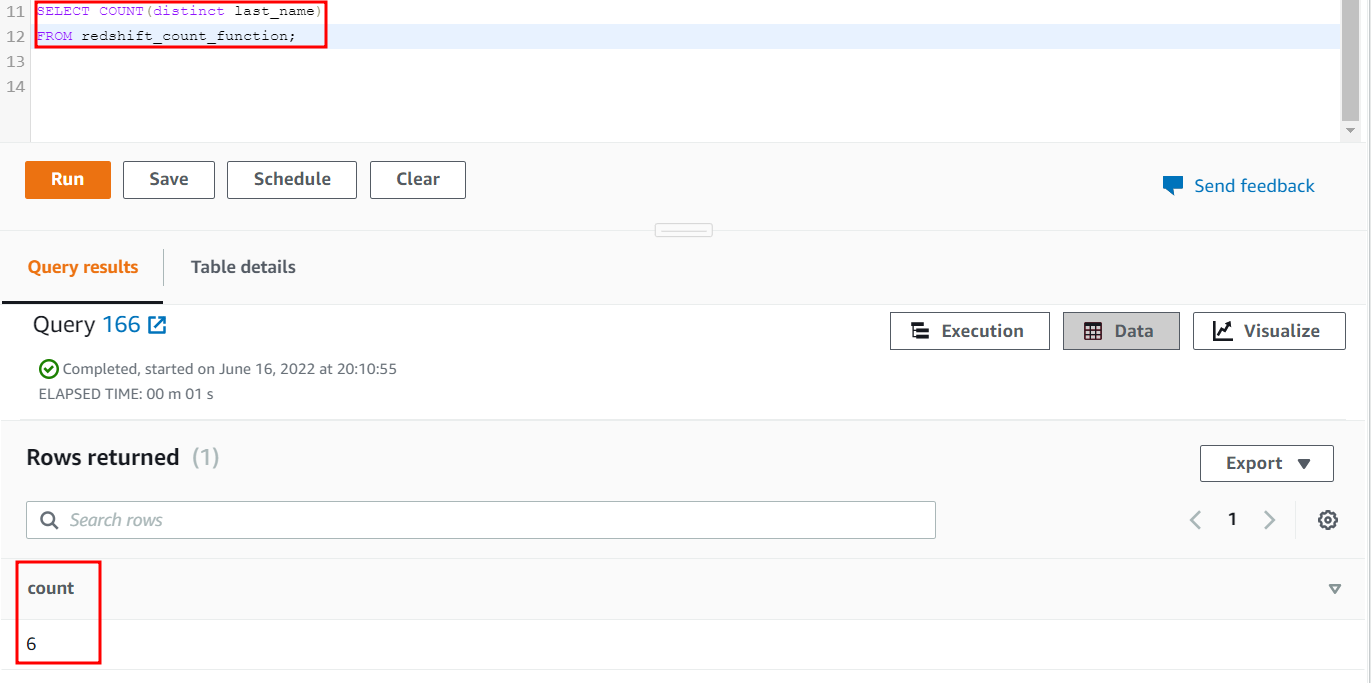
Apply the COUNT function using the DISTINCT parameter on the last_name column of the above table. There are only six DISTINCT rows, so the COUNT function will count only the DISTINCT rows.
FROM redshift_count_function;
The output of the previous query will be as follows when executed:
6
COUNT Function on NULL Rows Using DISTINCT Parameter
In this example, we will use the COUNT function on the column having a null row using a DISTINCT parameter.
| S_no | ID | first_name | last_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11 | Dwayne | Johnson |
| 2 | 22 | Vin | Diesel |
| 3 | 33 | Will | Smith |
| 4 | 44 | Robert | Downey Jr. |
| 5 | 55 | Chris | NULL |
| 6 | 66 | Will | Smith |
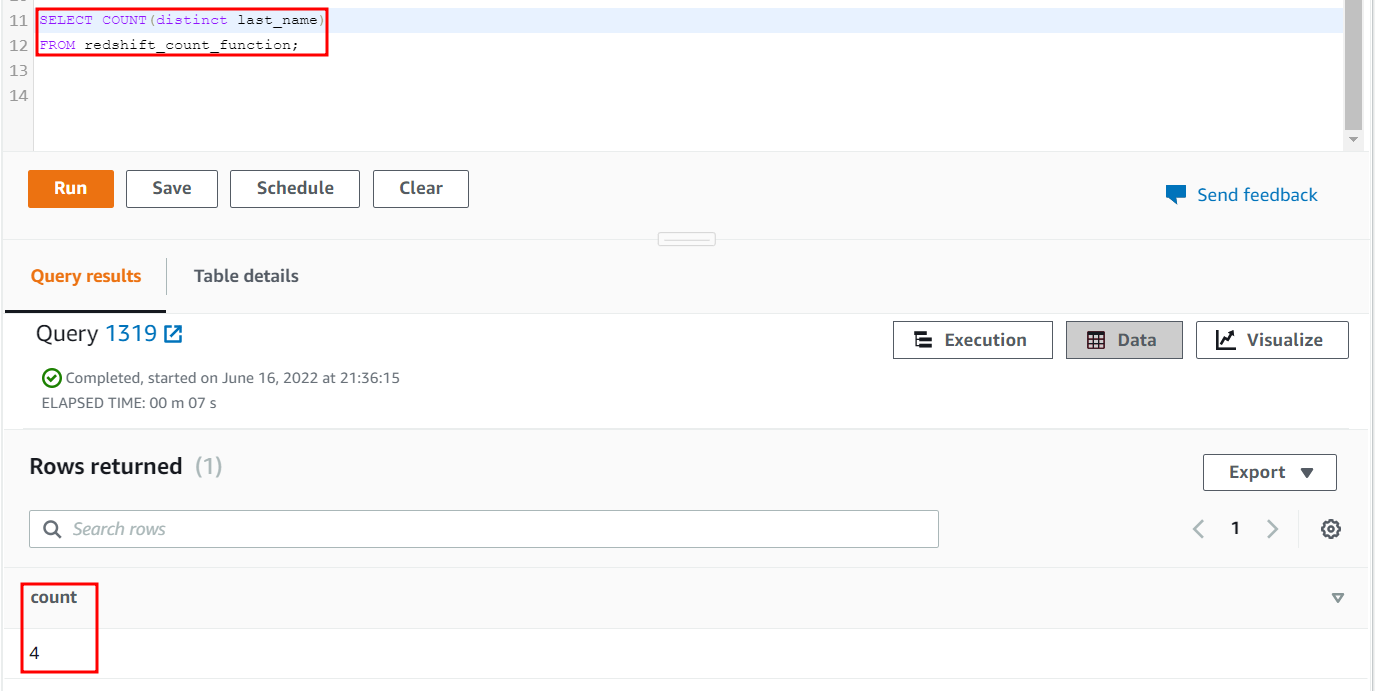
Apply the COUNT function using the DISTINCT parameter on the last_name column of this table. This will only count four rows because one row has a NULL, and one row has a duplicate value.
FROM redshift_count_function;
The output of the previous query will be as follows when executed:
4
Conclusion
In this article, we have studied how to use the COUNT function to count the number of rows returned by an expression. The COUNT function can be applied to count the total number of rows and the unique rows only by specifying the DISTINCT parameter. In order to count all the rows, including the NULL values, use the COUNT function with the (*) parameter.