Create Array
Different ways to create the PERL array have been shown in this part of this tutorial.
A. Create an Array by Initializing Values
The “@” symbol is used to declare a PERL array with values. The array values are separated by a comma with the first brackets in this type of declaration. Different arrays have been created by initializing the values in the following example.
Example
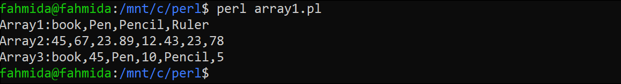
Create a PERL file with the following code that shows the way of declaring different types of arrays in PERL. Here, the first array contains 4 string values, the second array contains 6 number values, and the third array contains 3 strings and 3 number values. The values of three arrays have been printed by using the print operator. The join() function has been used to combine the array values with a comma (,).
@strArray = ("book","Pen", "Pencil", "Ruler");
#Define second array
@numArray = (45, 67, 23.89, 12.43, 23, 78);
#Define third array
@mixArray = ("book", 45, "Pen", 10, "Pencil", 5);
#Print array values
print "Array1:", join(',', @strArray),"\n", "Array2:", join(',',@numArray),"\n","Array3:", join(',',@mixArray),"\n";
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
B. Create an Array by Using the “qw” Operator
The “qw” operator is used to create a PERL array from a string value based on the white space. The “@” symbol is used to declare a PERL array like before. Different arrays have been created by using the “qw” operator in the following example.
Example
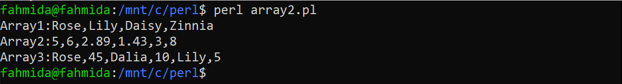
Create a PERL file with the following code that shows the way of declaring different types of arrays in PERL by using the “qw” operator. Here, the first array contains 4 string values, the second array contains 6 number values, and the third array contains 3 strings and 3 number values. The values of three arrays have been printed by using the print operator. The join() function has been used to combine the array values with a comma (,) shown in the previous example.
@strArray = qw\Rose Lily Daisy Zinnia\;
#Define second array
@numArray = qw\5 6 2.89 1.43 3 8\;
#Define third array
@mixArray = qw\Rose 45 Dalia 10 Lily 5\;
#Print array values
print "Array1:", join(',', @strArray),"\n", "Array2:", join(',',@numArray),"\n","Array3:", join(',',@mixArray),"\n";
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
C. Create an Array by Initializing Each Value Separately
Each value of the array can be initialized separately by mentioning the index value or adding a value without whitespace using the “qw” operator. The “$” symbol is used to set each value of the array. Different ways to create an array by adding a single value have been shown in the following example.
Example
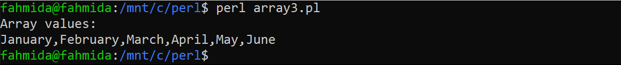
Create a PERL file with the following code that shows the way of declaring the value of an array by mentioning the index value. Here, four string values are added by using double quotes, and 2 string values are added by using the “qw” operator. The values of the array have been printed by using the print operator. The join() function has been used to combine the array values with a comma (,) shown in the previous example.
$months[0] = "January";
$months[1] = "February";
$months[2] = qw/March/;
$months[3] = qw/April/;
$months[4] = "May";
$months[5] = "June";
#Print the array values
print "Array values:\n", join(',', @months),"\n"
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
D. Create Sequential Array
The array of sequential values can be created by using the range values. The “@” symbol is used to declare the range array. Different types of range arrays have been mentioned in the following example.
Example
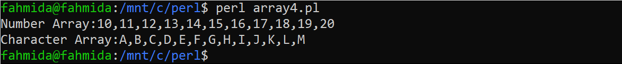
The sequential array values can be initialized by defining the range. Create a PERL file with the following code that will show the way of initializing array values by using numeric range and character range. The values of these arrays have been printed by using the print operator. The join() function has been used to combine the array values with a comma (,) shown in the previous example.
@numArray = (10..20);
#Declare array of sequantial characters
@charArray = (A..M);
#Print the array values
print "Number Array:", join(',', @numArray),"\n", "Character Array:", join(',',@charArray),"\n"
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
Access Array Values
All array values can be accessed by using the loop, and the particular array value can be accessed by mentioning the index value. The “$” symbol is used to print a particular array value. The following example shows different ways to access array values.
Example
Create a PERL file with the following code that shows the way of accessing array values in different ways. An array of string values has been defined in the code. Next, the 2nd and 3rd elements of the array have been accessed by mentioning the index value. The foreach loop has been used to access all values of the array and print each value in each line.
@strArray = ("book","Pen", "Pencil", "Ruler");
#Print individual value
print "The value of 2nd index: ",$strArray[1],"\nThe value of the 3rd index: ", $strArray[2],"\n";
#Print all array values
print "Array values are:\n";
foreach $value (@strArray)
{
print "$value\n";
}
Output
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
Conclusion
The way of creating and accessing the PERL array has been shown in this tutorial by using multiple PERL examples. I hope this tutorial will help the PERL users to know the purpose of using the PERL array properly.