In the situation of arrays, the only way to copy one array into another is to use an iterative approach, which involves running a loop and copying each element at its appropriate index. Fortunately, Vector classes include many ways for copying a whole vector into another in a more convenient manner.
Copying a vector implies creating a new vector that has a copy of all of the components in the original vector in the same order.
Example 1: Std::Copy Method To Copy Vector In C++
The std:: copy is a built-in function for copying items of one vector to the other. However, ensure that the target vector has enough space to hold all of the original sequence’s components.
The program has the header section with the required files. First, we have the iostream file; then, we have a vector file, a standard built-in library file in c++. Through this library, we can use vectors in the program. Next, we have an algorithm header file for copying elements of vectors. We have also included the iterator file in the program, which allows us to access the elements in the vectors.
Now, we have the main function where we have declared a variable as “vec1” of vector type and initialized it with the integer array. Next, we have declared another vector type variable as “vec2”. Then, invoked the copy function, which copies all the elements of “vec1” to “vec2”. The begin() function takes the first vector iterator, the end() function takes the last vector iterator, and the back_insertor here inserts the elements from the back.
Then we have for loop condition, which loops the cycle over each element stored in the “vec1” and prints the elements. The same is the case for “vec2” elements; it also iterates through the for loop cycle and will print on the prompt screen.
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iterator>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> vec1{ 3, 6, 6, 11 };
vector<int> vec2;
copy(vec1.begin(), vec1.end(), back_inserter(vec2));
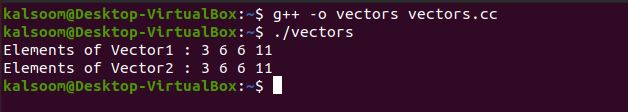
cout << "Elements of Vector1 : ";
for (int v=0; v<vec1.size(); v++)
cout << vec1[v] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "Elements of Vector2 : ";
for (int v=0; v<vec2.size(); v++)
cout << vec2[v] << " ";
cout<< endl;
return 0;
}
The above program’s output demonstrates that the vector was copied to the other vector.
Example2: Assign() Method To Copy Vector In C++
Another alternative is to use the vector class’s public member method assign(), which substitutes the vector elements with elements from the defined range.
We have included all the required files in the header section, which allows us to access the vector elements, copy the vector element and also allow us to use vectors in the program. In addition, the namespace std file is included in the program’s header.
The next step is invoking the main function in which program implementation has been done for execution. First, we have defined a vector type variable “a” which stores integers in an array pattern. Then, we have another variable, “b” also of vector type.
After defining the variable, we have used the assign() method, which returns the iterator pointing to the first and the last vector “a”. The assign method copied the vector “a” elements to the vector “b” elements. Now, the for loop is used to iterate over the vector “a” elements and will print the elements of vector “a”. The for loop is also used for the iteration on vector “b” elements and displays these elements through the cout command.
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iterator>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> a{3, 5, 7, 9 ,11};
vector<int> b;
b.assign(a.begin(), a.end());
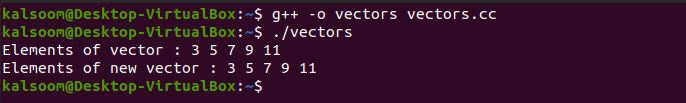
cout << "Elements of vector : ";
for (int i=0; i<a.size(); i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "Elements of new vector : ";
for (int i=0; i<b.size(); i++)
cout << b[i] << " ";
cout<< endl;
return 0;
}
The vector is copied to the other vector. Hence, we can also use the assign function in c++ to copy vector elements to the other elements of the vector.
Example 3: Assignment Operator Method To Copy Vector In C++
A vector can also be copied into another vector with the assignment operator. The reason why such an assignment operator works is that it just overwrites the existing members if any of these are accessible, otherwise assigns the item from where it is copied.
The first step has included essential files in the header section required for this program. Also, we have a namespace std file to use its function in the program. Then, we have the main function in which we have declared two variables, “vector1” and “vector2” of vector type. Only “vector1” is initialized with the integer array.
Now, we have an assignment operator (=) which copies the “vector1” items to the “vector2” items by simply placing the “=” operator in between the “vector1” and “vector2”. The for loop is used for the iteration over both the given vectors respectively and prints the items present in the specified vectors through the cout object.
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iterator>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> vector1{0 ,2 ,4 ,6 ,8};
vector<int> vector2;
vector2 = vector1 ;
cout << "vector1 elements : ";
for (int i=0; i<vector1.size(); i++)
cout << vector1[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "vector2 elements : ";
for (int i=0; i<vector2.size(); i++)
cout << vector2[i] << " ";
cout<< endl;
return 0;
}
The vector1 elements are copied to the vector2 elements as shown in the following prompt screen.
Example 4: Constructor Method To Copy Vector In C++
When a vector is declared, passing an existing initialized vector copies the items of the given vector into the newly declared vector. We have to provide a source vector to the destination vector as a constructor, which will then be called the copy constructor.
Starting with the header section, we have some standard built-in library files of c++ which are needed for this program. The main function is then invoked where we have declared a vector type variable as “p”. The variable “p” contains the array of integers. Then, declaring a new vector as “p” and passing an element from an existing vector “p” in the constructor method.
Through the constructor method, the vector “p” elements are copied to the vector “q”. The for loop is used for both the vectors “p” and “q” and will be printed on the prompt screen of Ubuntu.
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iterator>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> p{1996 ,1997 ,1998, 1999};
vector<int> q(p);
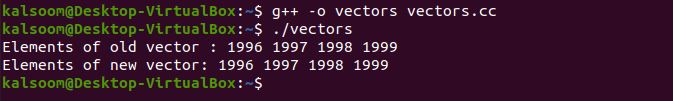
cout << "Elements of old vector : ";
for (int i=0; i<p.size(); i++)
cout << p[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "Elements of new vector: ";
for (int i=0; i<q.size(); i++)
cout << q[i] << " ";
cout<< endl;
return 0;
}
Hence, the elements are copied from the old vector “p” to the new vector “q” in the following screen.
Conclusion
We learned about many methods for copying a vector into a new vector. We have used four different approaches for copying vectors in c++. These approaches included the std:: copy method, assign method, assignment operator method, and a passing source vector as a constructor. With the proven results of these methods used in the program, we have copied the elements of the existing vector elements to the newly formed vector in the c++ programming language.