In this write-up we will learn the below listed aspects of Java objects:
- What is an Object in Java?
- How to Create an Object
- The . dot operator
- Example
So, let’s begin!
What is an Object in Java?
The below-listed concepts will provide you with a detailed understanding of the java objects:
- It is an instance of a class.
- It is a real entity that occupies the memory.
- An object must have a unique identity
- An object can have different states and behaviors.
- States represent the individual properties of that object and can be stored in the fields/variables.
- Object behavior can be described by the operations/actions that an object can conduct.
- If a class has multiple objects, then all the objects can share the same behaviors and states.
- An object is a physical entity.
- The objects are created at run time.
How to Create an Object
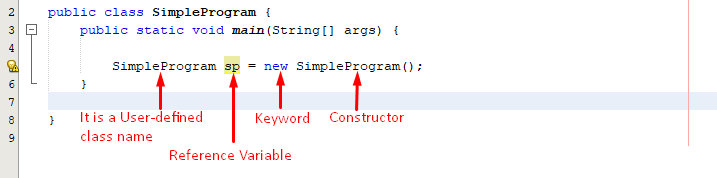
The below code block will provide you a profound understanding of object creation:
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleProgram sp = new SimpleProgram();
}
}
The above snippet shows the basic syntax of object creation in Java:
The entities specified on the left side i.e. “class name and reference variable” are collectively known as variable declaration.
While the entities specified on the right side i.e. “memory allocation/new keyword and constructor” collectively creates an object.
The . dot operator
In java the “.” dot syntax is used to access the class members (attributes and functions) in java. You can learn more about the java classes at the following links:
Now, let’s consider an example to understand how to access the class members in java:
Example
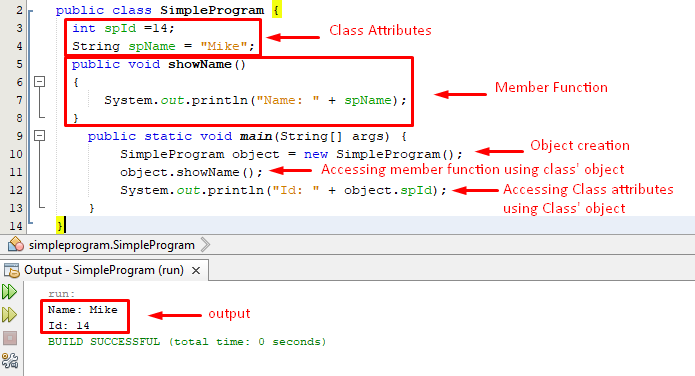
This example will explain how to create a java object and how to access the class members using the object of that class:
int spId =14;
String spName = "Mike";
public void showName()
{
System.out.println("Name: " + spName);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleProgram object = new SimpleProgram();
object.showName();
System.out.println("Id: " + object.spId);
}
}
In this example, we have a class named SimpleProgram that consists of two class attributes and a member function. We created an object of the class and accessed the class members using that object:
Output verified the working of the object.
Conclusion
An object is an instance of a class that occupies the memory. An object must have a unique identity and it can have different states and behaviors. The states represent the individual properties of that object and can be stored in the fields/variables. While the object’s behavior can be described by the operations/actions that an object can conduct. If a class has multiple objects, then all the objects can share the same behaviors and states. An object is a physical entity that can be created at run time. This article presents a comprehensive overview of objects in java with the help of appropriate examples.