Syntax:
The syntax of the force index is given below.
FROM table_name
FORCE INDEX (index_list)
WHERE condition;
Here, the index_list will contain one or more column names of the table_name used for searching.
Pre-requisites:
You have to create a database table with data in a MySQL database to check the Force Index feature of MySQL. Open the terminal and connect with the MySQL server by executing the following command.
Run the following command to create a database named test_db.
Run the following command to select the database.
Run the following query to create a table named employees with five fields.
`id` int(11) AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`post` varchar(25) NOT NULL,
`joining_date` date NOT NULL,
`salary` int NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(id));
Run the following INSERT query to add six values into the employees table.
(NULL, 'Nur Jahan', 'Assistant Manager', '2021-01-05', 78000),
(NULL, 'Asif Iqbal', 'Manager', '2019-03-20', 56000),
(NULL, 'Jafar Iqbal', 'Assistant Manager', '2021-12-31', '60000'),
(NULL, 'Sefali Akter', 'Marketing Officer', '2022-01-01', '65000'),
(NULL, 'Apurbo Chowdhury', 'CEO', '2013-05-15', '350000'),
(NULL, 'Nirob Hasan', 'Manager', '2019-12-18', '58000');
Example-1: Check the default index
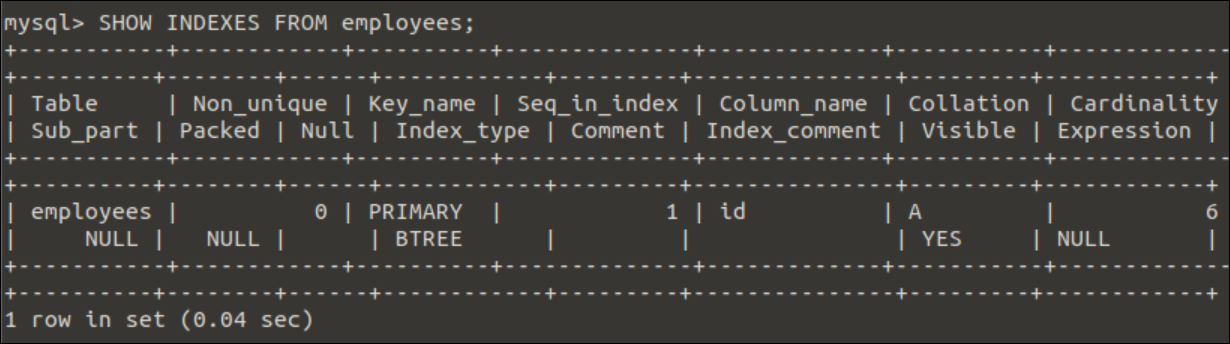
When a table is created, the primary key will be defined as an index by default. Run the following command to check the current index list of the employees.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query. The output shows that the BTREE index has been assigned for the id field of the employees table.
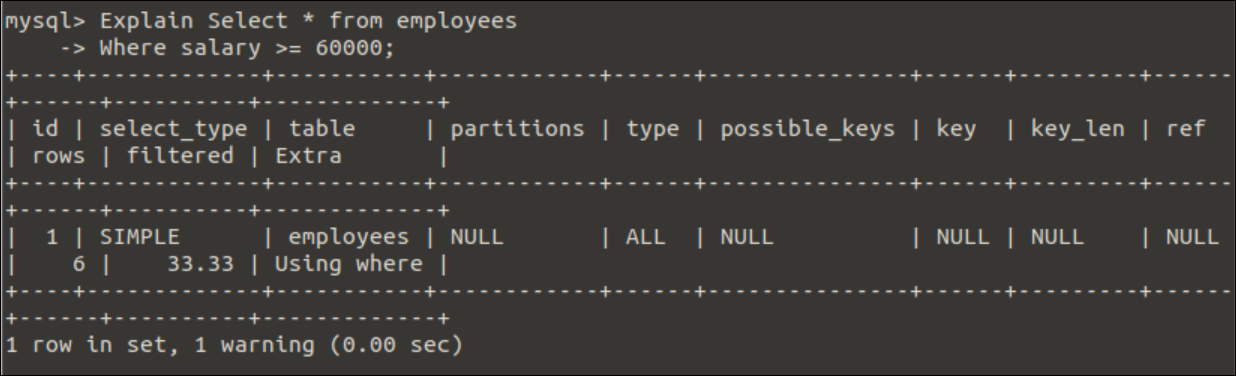
If no index is assigned for the salary field of the employees table after creating the table, then all records of the table will be scanned by the query optimizer for the following query. The Explain keyword is used here to get the execution information of the SELECT query.
Where salary >= 60000;
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query. The output shows that all rows were required to execute the query and filter data from the employees table.
Example-2: Check the execution of the query after creating the index
You have to define the index for the salary field of the employees table to optimize the query properly. Run the following query to create the index for the salary field of the employee table.
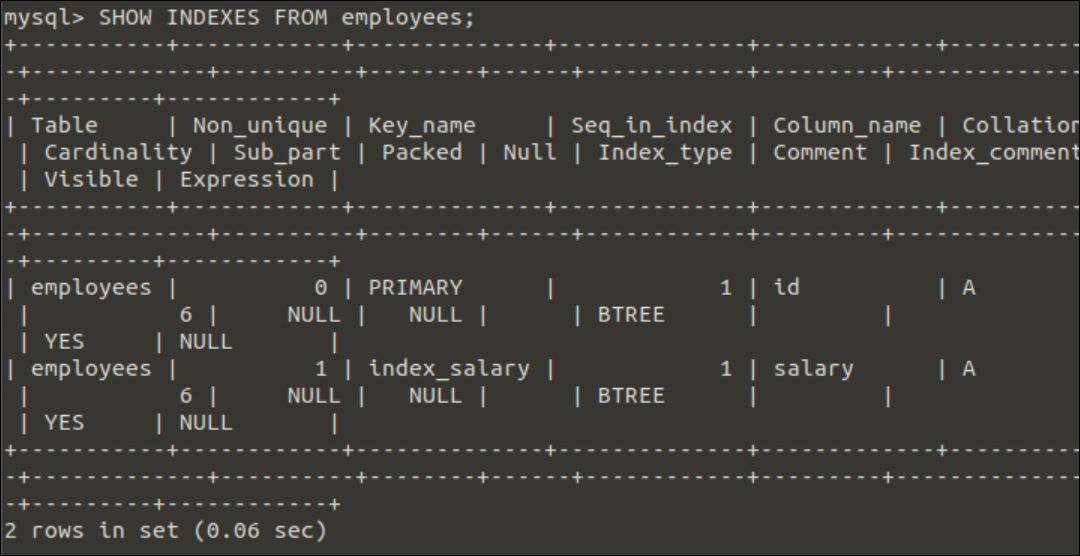
Run the following command again to check the current index status of the employees table.
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above command. The output shows that there are two BTREE indexes now in the employees table.
Run the previous SELECT query again to check the execution information of the query. The output of the Explain statement may not be accurate for the table containing few records or may vary for different executions. It is better to add large records into the table to get the approximately correct result.
Where salary >= 60000;
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query. The output shows that 4 rows were required to execute the query and filter the data from the employees table. According to the output, the query’s execution time is 0.04 seconds that accessed 4 rows to get the output.
Example-3: Check the execution of the query after using Force Index
The query optimizer will use the defined index or not that depends on the query’s condition, the number of records of the query, and the number of matching rows of the table based on the condition.
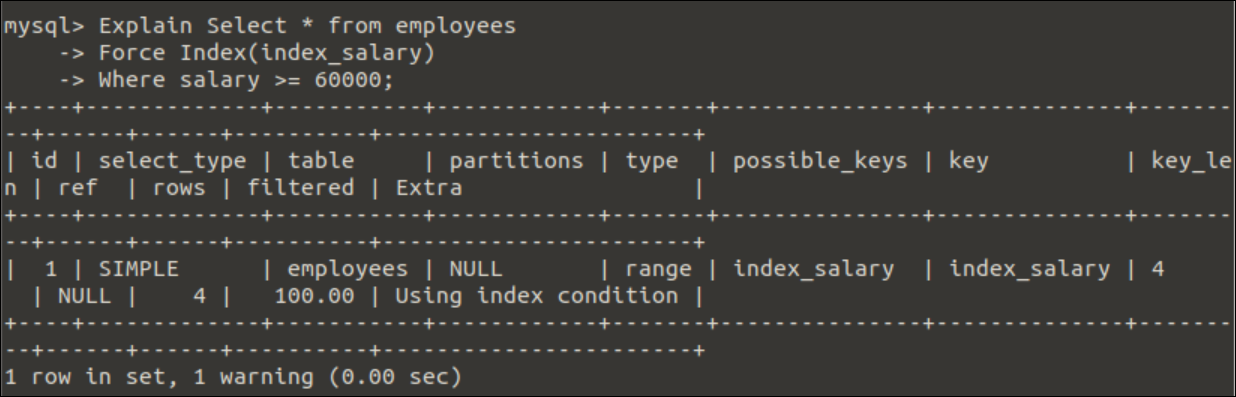
Run the following query to force the query optimizer to use the index_salary index at the time of query execution. The Force Index statement is used before the WHERE clause of the SELECT query to force the query optimizer to use the index_salary index.
Force Index(index_salary)
Where salary >= 60000;
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above query. The output shows that 4 rows were required to execute the query and filter the data from the employees table. According to the output, the query’s execution time is 0.00 seconds that accessed 4 rows to get the output. This output may also vary for different executions.
Conclusion:
The Force Index feature of MySQL is useful when searching the particular value in a table that contains a large number of records. The way of creating an index for a table and forcing the query optimizer to use that index forcefully at the time of query execution by using the Force Index statement has been shown in this tutorial.