Python programming often requires counting the number of times a value or element appears in a list. For instance, you might want to know how many times the word “Python” occurs in a list of programming languages, or how many times the number “1” appears in a list of binary digits. There are a number of ways to count occurrences in a list in Python.
The purpose of this Python guide is to explore different methods to count the occurrences in a list. Let’s start with the following contents:
Method 1: Count the Occurences in a List Using the “count()” Method
The “count()” method retrieves the number of times a given value or object appears in a list or string. This method is used in the below example to count the occurrences of a given list value.
Syntax
Here, “value” is the element to search from the list.
Example
Here is the code for counting the occurrences in the input list:
count = list_value.count(45)
print(count)
In the above code, the “count()” method is used to count the number of occurrences of the specified value i.e., “45” in the list.
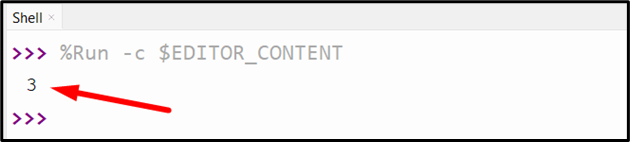
Output
The above output displayed the count of occurrences i.e., “3” against the value “45” in the list.
Method 2: Count the Occurences in a List Using the “Counter” Class
The “Counter” class is another way to determine how many times a value appears. It takes an iterable as a parameter and returns a dictionary containing the count for each element in the iterable. This approach can be applied to count the occurrences of all the list values.
Syntax
In the above syntax, “iterable_or_mapping” is an optional argument that can be a sequence of elements, a dictionary including keys and counts, or keyword arguments mapping string names to counts.
Example
The below code is used to determine how many times each value can be found in the list:
list_value = [45, 15, 45, 45, 11]
count = Counter(list_value)
print(count)
In the above lines of code:
- Firstly, the “Counter” class is imported from the module named “collections”.
- After that, the “Counter” class is applied to return the count of the occurrences of all the list values by taking the defined list as its argument.
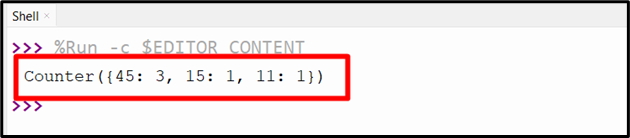
Output
As seen, the number of occurrences of all of the values in the list has been displayed.
Note: The “Counter” class approach is faster than the “count()” method since it does not have to iterate over the entire list multiple times.
Method 3: Count the Occurences in a List Using the “operator” Module
The “operator.countOf()” function of the “operator” module returns the count of the value in the given list. This approach can be applied to return the count of the occurrences of the specified list value.
Syntax
In the above syntax:
- “sequence” indicates the sequence in which to count the occurrences of the element.
- “element” signifies the element of which the occurrences need to be counted.
Example
Let’s overview the following example:
list_value = [45, 15, 45, 45, 11]
count = operator.countOf(list_value,45)
print(count)
In the above code snippet:
- Firstly, the “operator” module is imported.
- After that, the “countOf()” function accepts the list and the specified list value as an argument, respectively, and returns the count of occurrences of the particular value in the list.
Output
The above output displays the occurrences of the specified value i.e., “45-> (3 times)” in the given list.
Method 4: Count the Occurences in a List Using the “List Comprehension” Approach
The “List Comprehension” approach is utilized in the Python program to create a new list from its existing elements/items. In this example, this approach can be used with the “if” statement to count the occurrences of a particular list value.
Syntax
Example
This code counts the occurrences of the specified value in the input list:
count = [i for i in list_value if i == 45]
print(len(count))
In the above code block:
- Apply the “List Comprehension” approach such that the “for” loop is used along with the “if” statement to iterate over the list and count the occurrences of the specified value i.e., “45”.
- The list comprehension then returns a new list that shows the number of occurrences of the specified value.
- Lastly, the “len()” function is used to get the length of the occurrence list and retrieve the count of the occurrences.
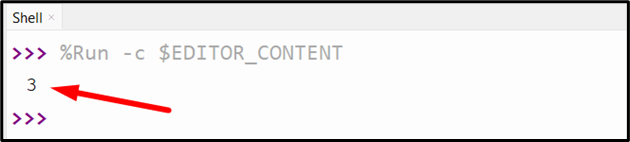
Output
In the above output, the total occurrences of the specified value have been returned accordingly.
Method 5: Count the Occurences in a List Using “for” Loop
The “for” loop can also be used along with the “if” statement and “+=” operator to count the total occurrences of the specified value in a list.
Example
Let’s overview the following example code:
count = 0
for i in list_value:
if i == 45:
count += 1
print(count)
Apply the following steps in accordance with the above lines of code:
- First, the “list” is initialized and the “0” value is assigned to the variable “count” to count the occurrences.
- Now, the “for” loop is utilized along with the “if” statement to iterate through/over the given list and count the occurrence of the specified value.
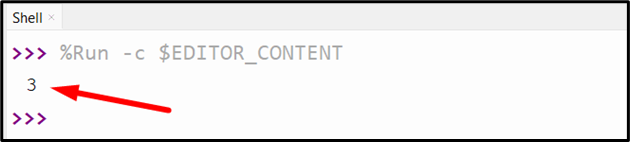
Output
This output implies that the total occurrences of the specified value in the list are “3”.
Conclusion
To count the occurrences in a list in Python, apply the “count()” method, “Counter” class, “operator” module, “List Comprehension” approach, or the “for” loop. These approaches either count the occurrences directly or via iterating through the list. Also, the occurrences of a particular as well as all the values in the list can be counted. This post offered various ways to count occurrences in a list using numerous examples.