Struct Syntax:
The structure declaration is shown in the image below. It starts with the keyword “struct” along with any structure name that has been given to it. Within the body of a structure, we can define many variables of any type. The structure body would be closed with “;”. To pass a function, we will be using two methods in this guide. Let’s look at both methods.
Example 01: Pass Structure to a Function by Value
The first method to pass a structure to a function is via the value. Let’s use this method to create a C file in the shell using a touch query.
After creating a file, you must open it in some editor, i.e., GNU nano editor, using the command stated below.
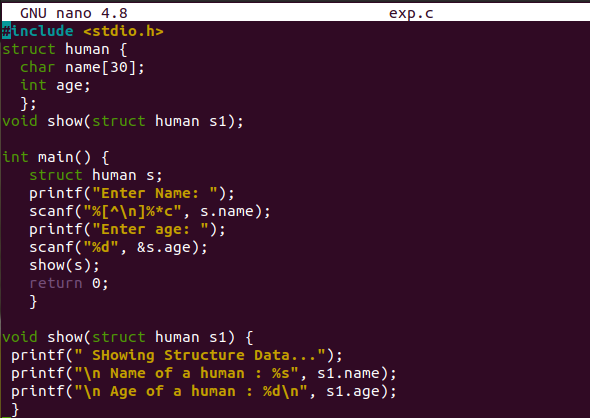
After the file gets opened, write the code within the file as shown in the image. The first line contains the header. A structure “human” has been declared with two variables. One is the character variable “name” of size “30”. Another is an integer type variable used to store the age of a human. The input has been provided by a user at run time using the scanf method. This input has been saved to the structure’s variables using the objects. After that, the structure has been passed to the user-defined method show() as an argument. It’s a function call to method show(). The show method has been taking structure in its parameter as value. The structure variable values have been displayed on the console via the printf statement used within the user-defined function show().
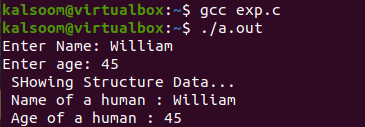
Save your file using the Ctrl+S shortcut key. After that, I came back to the terminal using the “Ctrl+X” shortcut. We have to compile the above-stated code first. The “gcc” compiler has been utilized for this purpose. In the end, the execution of a file takes place. The user has added its name and age. The structure has been passed to show() method as value. The structure values have been displayed below.
$ . /a.out
Successful output can be seen on the terminal window of Ubuntu 20.04.
Example 02: Pass Structure to a Function by Reference
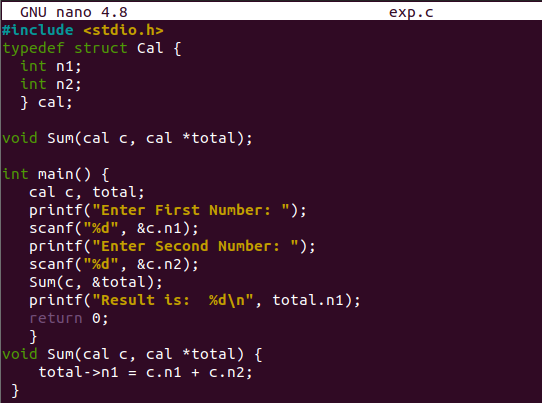
Now, let us start with this illustration. Within this example, we will be looking at the structure that will be passed to a user-defined method via reference. In this method, the whole structure or values have not been passed to another function. The variable’s memory address of structure would be passed to the method as a reference. So, we have opened the same file, “exp.c” to update it. Included the input-output standard header. We have created a new structure named “Cal” having two integer type variables n1 and n2. The reference object of the “Cal” structure has been created. The function prototype of the “Sum()” method has been declared before the main method.
The main function contains the scanf() method to contract input from the user at execution time. The values have been passed to the structure variables by reference using their memory addresses. The “&” sign has been used here for binding the memory addresses of structure variables with the values entered by the user. The address and values of a variable object “c” and “total” have been passed to the function “sum” as a reference.
The function “Sum” has been getting the values of structure variables n1 and n2 by reference of object “c” and adding them up. The resultant values have been saved to the variable n1. The main method displays the sum of both variables.
Compile and run the code. The user added two numbers, and the sum of both numbers was displayed. The gcc and “a.out” commands have been utilized here.
$ . /a.out
Successful output can be seen on the terminal window of Ubuntu 20.04.
Conclusion:
This article contains the implementation of a passing structure to a user-defined function in C language. Two approaches have been utilized for this purpose, i.e., by value and reference. While learning how to pass a struct to function in the C programming language, you can utilize both methods. We hope this article will assist you at its best to understand the concept of passing structure to any user-defined function in C programming.