In this post, we are focusing on finding the NTP server by installing and configuring the NTP in Debian.
How do I find my NTP server on Debian
NTP is a process in which the client machine requests the server to set its time. So first we will understand how to install and configure the NTP server then will learn how to find out the IP addresses of NTP.
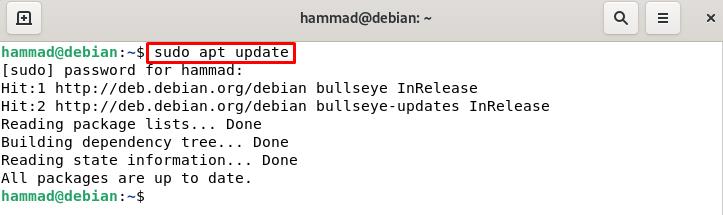
Installation and Configuration of NTP : First, we will update Debian’s repository:
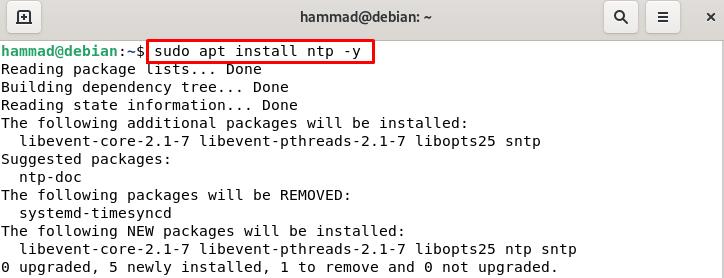
We will install the latest package available of NTP:
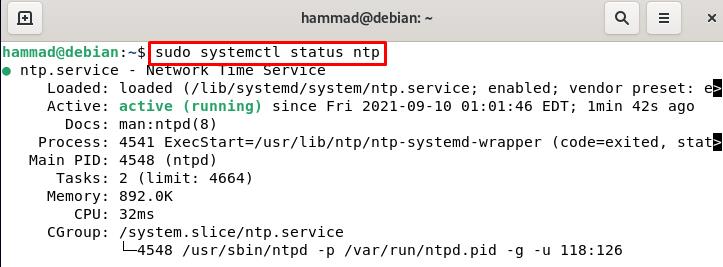
By default, after the installation, NTP should be of active status, you can confirm it by checking its status but if it is inactive, you can start the NTP server:
After restarting, check its status whether it is running or not:
Hence the NTP is running. Now, we will configure the firewall so it will allow the client to request the server else it will restrict the client to send any query and for this purpose will first go to the root mode.
Run these two commands here, asking the firewall to allow the queries on port 123 which is by default allocated to the NTP.
iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 123 -j ACCEPT
Now we will exit the root user mode as:
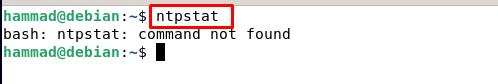
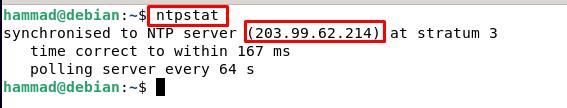
Verification of the NTP working using ntpstat : The ntpstat command shows us whether the connection is established between the server and client, if the connection is established, then the status will be “synchronized”. If ntpstat generates the error of “command not found” on running the command:
Then we can install ntpstat running the following command.
Now to check the status, again run the command.
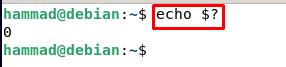
The output shows the NTP server IP address along with the recent details of the correction of time with the server and to verify the status of synchronization of the clock we will run the command to get the exit status.
The outcome “0” means the client’s clock is synchronized with the server. The other outcomes can be either “1” which means the clock of the client machine is not synchronized with the server or “2” which means the client is not connected to the server.
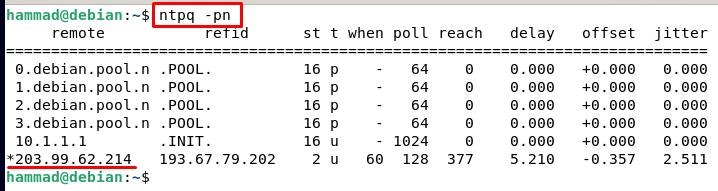
Checking the ntp server using ntpq command : Ntpq command monitors the NTP daemon, ntpd operations, and determines the performance of the NTP. We will use flags, p which means print the entire list of the peers known by the server with the summary of their state, and n which means display the host addresses.
Conclusion
NTP enables us to synchronize with the same time units that the world is following. NTP sets the time of its machine by asking the server to give it time information and then both are synchronized with the time of the internet. In this post, we have discussed two methods by which we can get the information about our NTP server in Debian. Hope this post will help you understand not only how to find our NTP server on Debian but also the installation and configuration of NTP on both server and client’s machine.