Linux is a powerful multi-user operating system. It can have many concurrent users accessing the system at the same time. The system admin can manage permissions for each user to specify which user can access what part of the system.
This guide will demonstrate how to create a new user with a different home directory in Linux.
User home directory
In Linux, each user gets its own home directory with exceptions like various system accounts. The home directory is a dedicated directory for the particular user to store the user-specific files. It’s also referred to as the “login directory”. Whenever logging in, the user will land on the respective home directory.
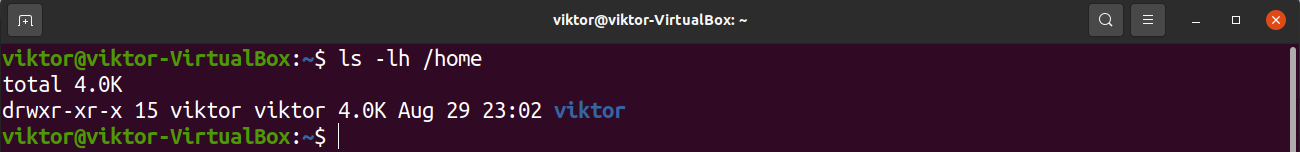
By default, all the users in the system have their home directories located at the following location.
Each home directory is named after the username of the user. For example, the home directory for the user “viktor” will look like this.
However, we can establish a different location for the user directory. It can be set during the creation of the user account or moved later.
Creating a user with a different home directory
Creating a new user
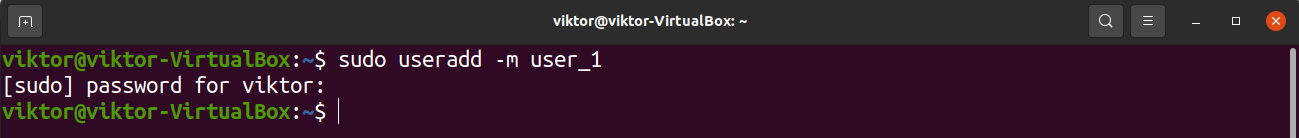
Each Linux system comes with useradd, a dedicated tool to create and update user accounts. It’s only available to the root user and non-root users with sudo privileges.
To add a new user to the system, run the following useradd command. The flag “-m” tells useradd to create a dedicated home directory for the new user. If not used, then the user won’t have a dedicated home directory.
The user is added to the system. The user is also registered to various database files (/etc/passwd, /etc/shadow, /etc/gshadow, and /etc/group).
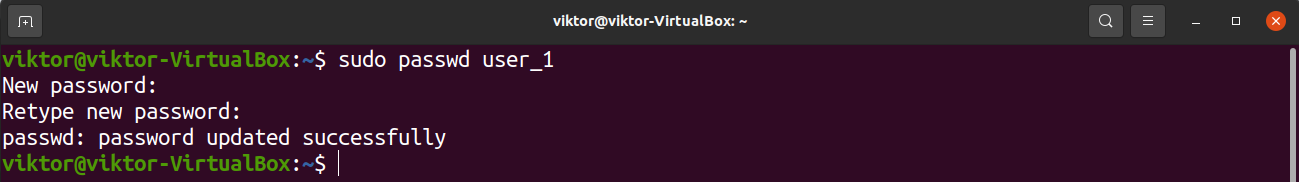
The user isn’t accessible yet. The following command will assign a login password for the new user.
The user is ready and fully functional. Access the new user.
Check the location of the home directory of the new user.
Creating a user with a custom home directory
By default, useradd will create the user’s home directory under “/home”. To specify the home directory in a different location, use the flag “-d”. Note that the directory must exist beforehand.
As always, use passwd to assign a login password for the new user.
Verify if the new user has a different home directory.
Moving existing user home directory
We can also assign a different home directory for an existing user. It will not move the contents of the existing home directory automatically to the new location.
Create a new directory. It will be the new home directory of an existing user.
Allow the new user complete access over the new directory.
Move all the contents of the existing user home directory to the new one.
Assign the new directory as the home of the user.
Verify the change.
Final thoughts
The home directory is an important part of a normal user account on Linux. This guide demonstrates how to assign a custom home directory to a new and existing user. These methods apply to any Linux distro.
Happy computing!