This tutorial will show you how to create an index on a MySQL table for both existing and new tables.
Before we get to execute queries and create indices, let us look at a few MySQL index concepts.
Types of MySQL Indices
MySQL supports two types of indices:
- A primary or Clustered index
- Secondary Index
MySQL automatically creates an index, called PRIMARY, any time we create a table with a PRIMARY KEY. Depending on the Database Engine, if the Primary Key or Unique key is not available in a table, MySQL may create a hidden key on the column with id values.
The primary index created by MySQL is stored together with the data in the same table. Other indices that exist within a table apart from the PRIMARY index are known as secondary indices.
How to Add an Index to an Existing Table
Although MySQL recommends adding an index during table creation, there are some instances where you may need to add an index to an existing table, such as in a regularly accessed column.
To add an index to an existing table, we can use the ALTER query.
Let us take a sample database with the tables as shown in the query below:
USE mysql_indices;
CREATE TABLE treks(
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
cpt_name
VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
ship
VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO treks(cpt_name, ship)
VALUES ('Carol Freeman', 'USS Cerritos'),
('Christopher Pike', 'USS Discovery'),
('Jean-Luc Picard', 'USS Enterprise'),
('James T. Kirk', 'USS Enterprise'),
('Jonathan Archer', 'USS Enterprise');
In the example above, MySQL will create an index key using the id column because it is specified as the PRIMARY KEY.
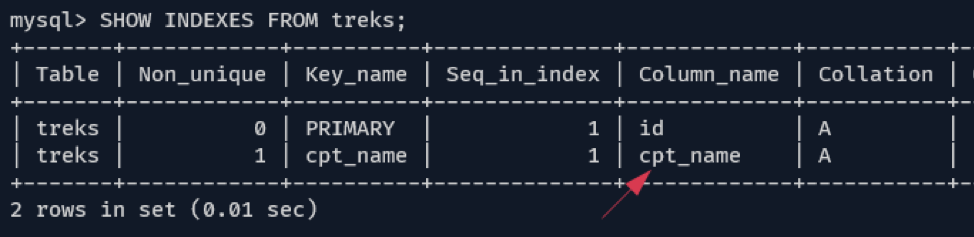
You can verify this using the query:
To create a custom index, use the ALTER query as:
In the above example, we use the cpt_name as the second primary key. To show the indices, use the query:
If not specified, MySQL will default any index as a B-TREE. Other supported index types include HASH and FULLTEXT.
The index type will depend on the Storage Engine for the specified table.
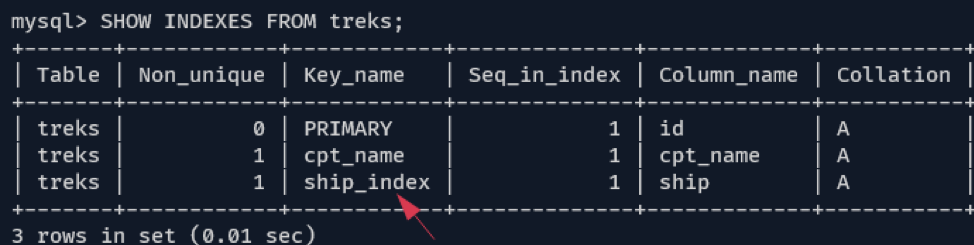
To create an index for a column or list of columns, we use the CREATE INDEX query. For example, to create an index for the “ship: column, we can do:
If we run the SHOW INDEX query on the table, we should see an index called “ship_index” on the “ship” column.
How to Add an Index to a New Table
The recommended way is to create an index or indices when creating a table. To do this, specify the columns to use as indices inside the INDEX () query.
Let us start by dropping the treks table in the previous example:
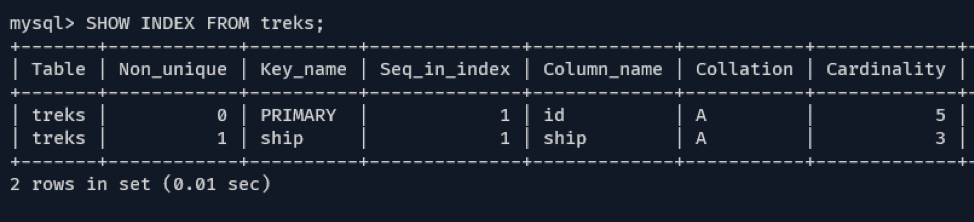
Next, let us recreate the table and specify the INDEX during creation. An example query is:
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
cpt_name
VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
ship
VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
INDEX (ship)
);
INSERT INTO treks(cpt_name, ship)
VALUES ('Carol Freeman', 'USS Cerritos'),
('Christopher Pike', 'USS Discovery'),
('Jean-Luc Picard', 'USS Enterprise'),
('James T. Kirk', 'USS Enterprise'),
('Jonathan Archer', 'USS Enterprise');
In the example query above, we add the ship column as an index during table creation. Since the id is the PRIMARY KEY, MySQL automatically adds it as an index.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to add an index to an existing table, add an index for a column, and create an index during table creation.