What are XML and HTML Documents?
HTML documents are any document that contains Hypertext Mark Language, which is the basic format used to describe the structure of documents displayed on the web.
Similarly, XML documents are documents that contain XML markup. According to the official documentation, XML or Extensible Markup Language is a markup language that defines the rules for encoding documents for both human and machine readability.
HTML and XML documents end in .html and .xml, respectively.
Installation
Before we can process any XML or HTML documents in Ruby, we need to install the XML/HTML parser library. In this example, we shall use the Nokogiri library.
To install it, use the gem package manager command:
Fetching nokogiri-1.12.0-x86_64-linux.gem
Successfully installed nokogiri-1.12.0-x86_64-linux
Parsing documentation for nokogiri-1.12.0-x86_64-linux
Installing ri documentation for nokogiri-1.12.0-x86_64-linux
Done installing documentation for nokogiri after 1 seconds
1 gem installed
Once installed, you can test it by launching the Ruby Interactive Shell with the IRB command.
Next, import the package as:
=> true
Loading HTML/XML Docs
To load HTML or XML documents using the Nokogiri library, you use the Ruby namespace resolution operator and access the loader, either the HTML or XML.
For example: To load HTML, use:
html_data = Nokogiri::HTML('
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
<</html>')
puts html_data.class
The example code should load the HTML contents and save them to the defined variable. To check the source class of the data, we use the .class method.
The code should display the output as:
Loading from File
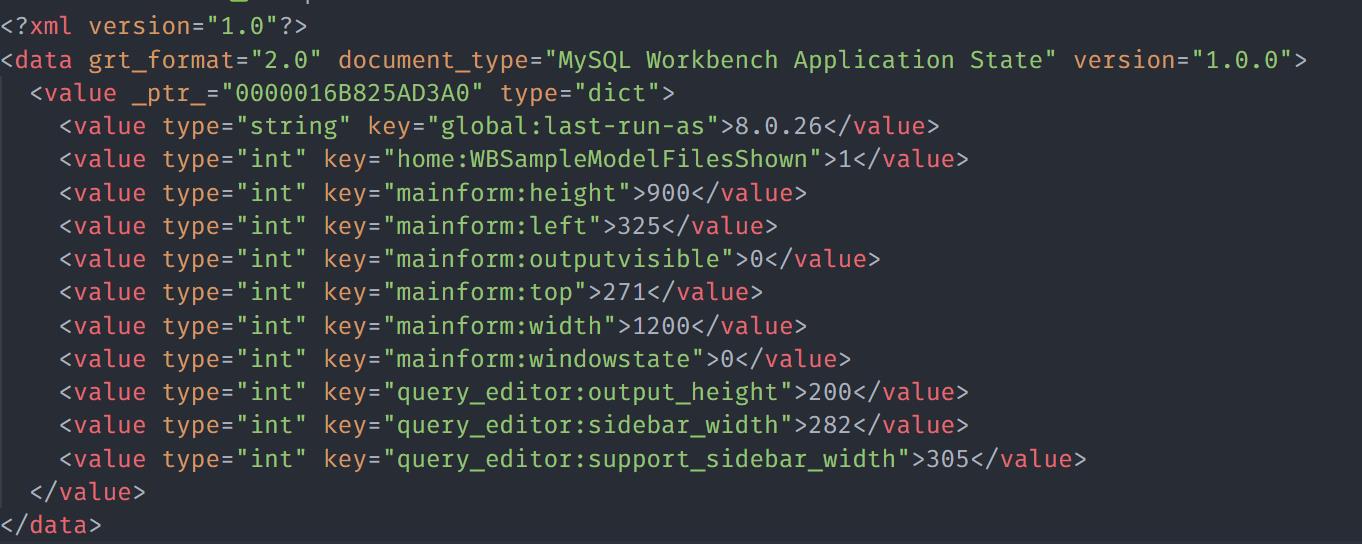
We can also load the data from an HTML/XML file. Consider a sample file with the XML contents as:
To load the XML File with Nokogiri, you can use the example code as shown:
sample_data = File.open('sample.xml')
parsed_info = Nokogiri::XML(sample_data)
puts parsed_info
Searching an XML document
To search a loaded XML or HTML document, we can use the XPath method.
For example: In the sample XML file above, to get all the values, we can do:
sample_data = File.open('sample.xml')
parsed_info = Nokogiri::XML(sample_data)
puts parsed_info.xpath("//value")
The sample code above should return the values with the value keyword.
Get Individual Item
We can also get the value of an individual item. For example: To get the document, type in the example XML file above:
sample_data = File.open('sample.xml')
parsed_info = Nokogiri::XML(sample_data)
puts parsed_info.xpath("/*/@document_type")
The code should return the value from the document_type.
Convert XML to HTML
You can also convert a parsed XML document to HTML using the to_html method. Here is an example code:
sample_data = File.open('sample.xml')
parsed_info = Nokogiri::XML(sample_data)
zero = parsed_info.to_html
puts zero
This should return the XML data to HTML in the form of a string.
Conclusion
This short tutorial has shown you how to parse XML documents using the Nokogiri package. Refer to the documentation to discover its full capabilities.