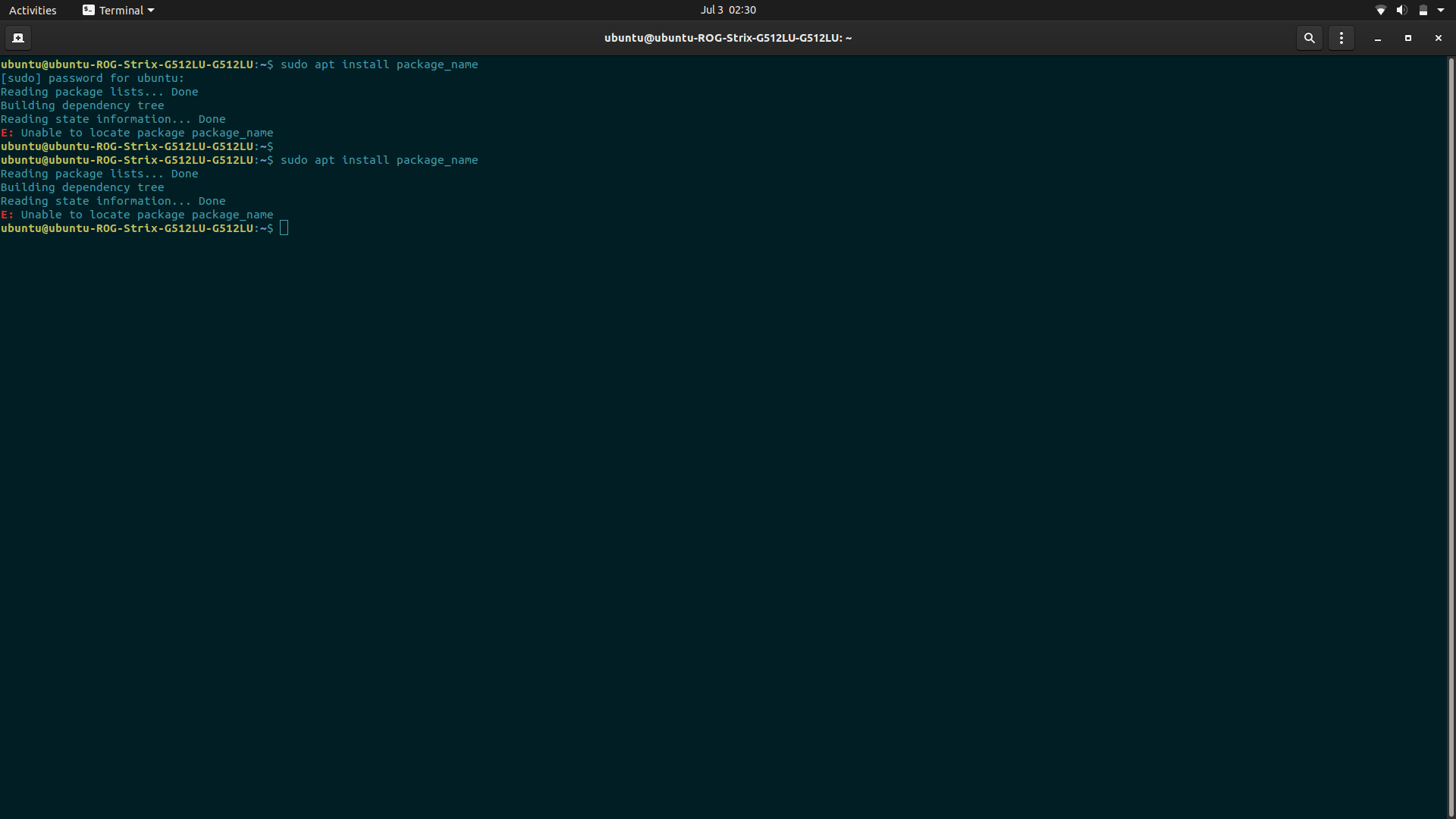
Why the “Unable to Locate a Package” Error Occurs?
This error usually occurs when a user tries to install a specific package. Still, you end up having this error because Linux could not find the package you were trying to install.
Many people surf the internet to answer “how do I fix Ubuntu unable to locate a package?”. If you are one of them, then don’t worry and read this guide thoroughly because we will give you the best possible way to tackle this error quickly.
How to Fix Ubuntu Unable to Locate a Package
This is the first thing you need to do when you have this error, recheck if you correctly typed the package name. Linux is also case sensitive, so you also need to check whether you have typed that correctly. For example, you tried to install “gimp,” and you typed “gmip” instead of gimp.
If it is your first time using Ubuntu, then execute the following command:
This command creates a local cache of available packages rather than updating Ubuntu directly.
When the “install” command is used, the apt package searches the cache to get the package and all the information about it like version, build, etc., and download it from its repositories over the internet connection. If the package is not found in the cache, you will get an error, and your system won’t install it.
Fresh installed Ubuntu has an empty cache, which means the package won’t be found and installed. So even if you haven’t installed it fresh, it is better to run the update command.
Check the Package’s Availability for your Ubuntu Version
If you still face this error, then it might be possible that the repository of that particular one is not available.
There can be two possibilities: either that package is unavailable for that Ubuntu version, or the package is available in the Universe repository, but the system hasn’t enabled it.
Please don’t get confused by these terms because we will clear everything for you. You need to check the current Ubuntu version by this command:
The output will be the version number of Ubuntu and the codename. Codename holds importance like using version 20.04, and codename is focal (you might have something else).
Now you have information about Ubuntu so go to the Ubuntu packages website. After that, scroll down and hover to the search menu. Enter the package name in your keyword section and then select the correct distribution codename. The section should be set to ‘any’. Now enter these details and click on the search button to proceed. It will provide complete information about whether that particular package is available or not.
In case it is available, then you can check which repository it belongs to. Sometimes the package is available in-universe repository. So, you need to enable universe and multiverse repositories through the following command:
Now, update the cache using the update command and try to install the package again.
Verify that Your System has Active Release of Ubuntu
Ubuntu releases mainly have two types: the long-term release with the support of 5 years and the regular release with the support of 9 months.
So you can check it by executing this command:
Now you can verify your system support date, and if the system is supported well and good, get a newer supported version.
If Nothing Above Mentioned Works
In this case, check the project’s official page because maybe it can get discontinued, and you are trying to install it. Suppose the Ubuntu packages website shows that a package is not available for that particular version. In that case, you must use other ways to install a package.
Conclusion
Handling Ubuntu errors might be a headache but follow our tutorials and guides, and we will help you through this. We hope that your error must be resolved in the way which we have mentioned above. Make sure you follow every step carefully to fix this error as soon as possible.