Example-1: Sort a list of numerical string data
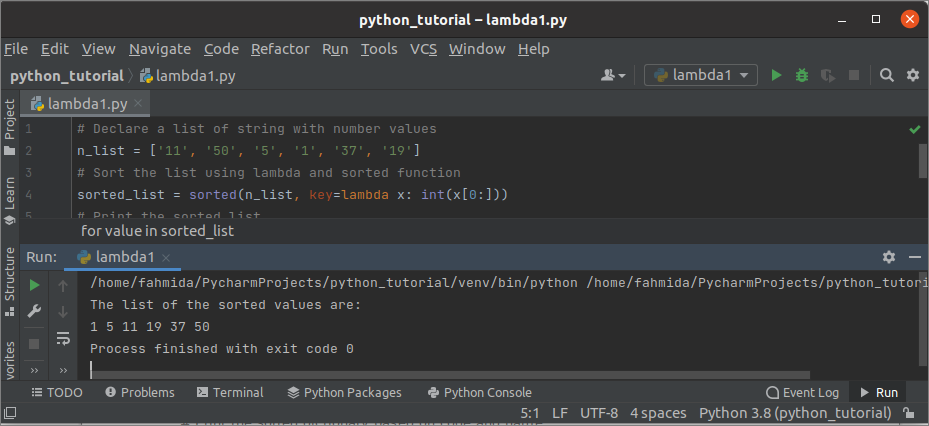
Create a python file with the following script to sort a list of string data using lambda that contains all number values. A list of 6 items has been defined in the script. Here, lambda has used inside the sorted() function to sort the list. The list variable has been given as the first argument value, the lambda has been set as the key value, and the starting position of the sort has been set in the third argument. Next, the print() function has used to print the sorted list with space.
n_list = ['11', '50', '5', '1', '37', '19']
# Sort the list using lambda and sorted function
sorted_list = sorted(n_list, key=lambda x: int(x[0:]))
# Print the sorted list
print("The list of the sorted values are:")
for value in sorted_list:
print(value, end=' ')
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script.
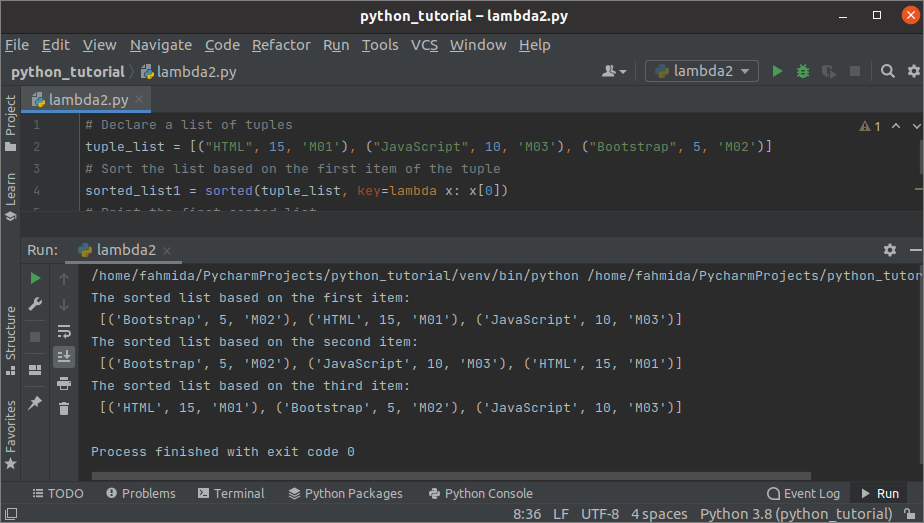
Example-2: Sort a list of tuples
Create a python file with the following script to sort a list of three tuples using lambda, where each tuple contains three items. Three types of sorting have been shown in the script. The sorting position is set to 0 in the first sorted function. This will sort the list based on the first item of each tuple. The sorting position is set to 1 in the second sorted function. This will sort the list based on the second item of each tuple. The sorting position is set to 2 in the third sorted function. This will sort the list based on the third item of each tuple.
tuple_list = [("HTML", 15, 'M01'), ("JavaScript", 10, 'M03'), ("Bootstrap", 5, 'M02')]
# Sort the list based on the first item of the tuple
sorted_list1 = sorted(tuple_list, key=lambda x: x[0])
# Print the first sorted list
print("The sorted list based on the first item:\n", sorted_list1)
# Sort the list based on the second item of the tuple
sorted_list2 = sorted(tuple_list, key=lambda x: x[1])
# Print the second sorted list
print("The sorted list based on the second item:\n", sorted_list2)
# Sort the list based on the third item of the tuple
sorted_list3 = sorted(tuple_list, key=lambda x: x[2])
# Print the third sorted list
print("The sorted list based on the third item:\n", sorted_list3)
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script. Three sorted lists of the tuples have shown in the output based on the sorted position.
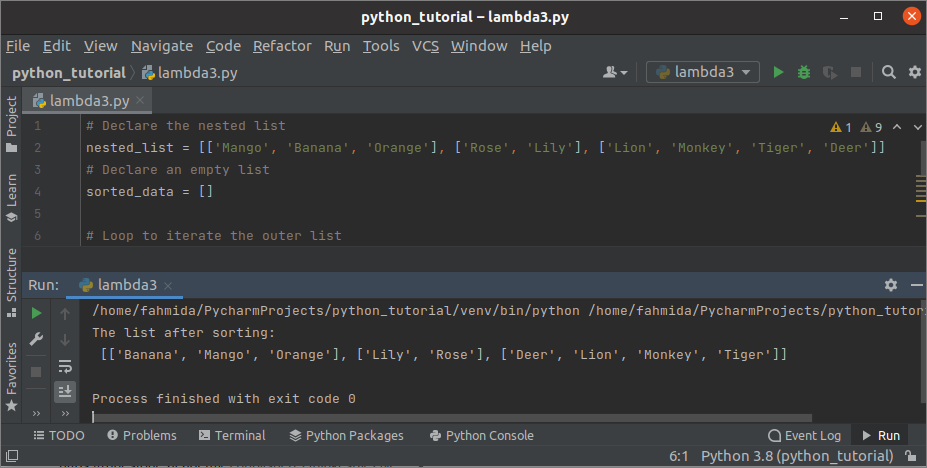
Example-3: Sort a list containing another list
Create a python file with the following script to sort the nested list using lambda. An empty list has been declared to store the values of the sorted list. Here, the nested ‘for’ loops have used to sort the items of the nested list. The outer ‘for’ loop will iterate based on the number of inner lists defined in the main list. According to the script, three inner lists as defined in the main list where the first inner list has three items, the second inner list has two items and the third inner list has four items. The inner ‘for’ loop will iterate based on the items of each inner list. The sorted() function has called with the lambda inside the inner loop to sort the nested list.
nested_list = [['Mango', 'Banana', 'Orange'], ['Rose', 'Lily'], ['Lion', 'Monkey', 'Tiger', 'Deer']]
# Declare an empty list
sorted_data = []
# Loop to iterate the outer list
for i in range(len(nested_list)):
# Loop to iterate the inner list
for j in range(len(nested_list [i])):
# Sort the inner list
sorted_list = sorted(nested_list [i], key=lambda x: x[0])
# Append the sorted list
sorted_data.append(sorted_list)
# Print the sorted nested list
print("The list after sorting:\n {}".format(sorted_data))
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script. The list of three sorted lists has shown in the output.
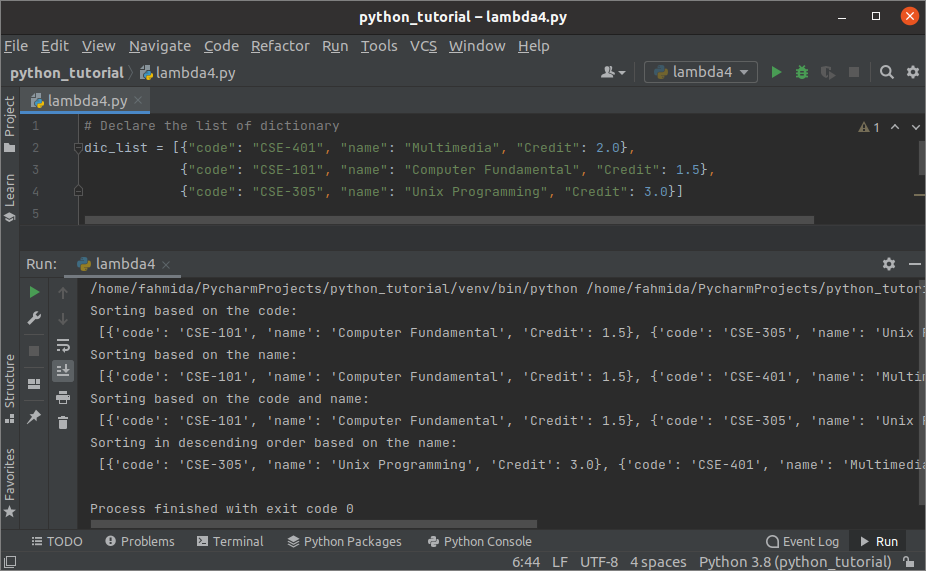
Example-4: Sort a list of dictionaries
Create a python file with the following script to sort a list of dictionaries using lambda. Each dictionary contains three key-value pairs inside the list. Four types of sorting have been shown in the script. The first output will show the sorting based on the code key. The second output will show the sorting based on the name key. The third output will show the sorting based on the code and name keys. The fourth output will show the sorting in descending order based on the name key.
dic_list = [{"code": "CSE-401", "name": "Multimedia", "Credit": 2.0},
{"code": "CSE-101", "name": "Computer Fundamental", "Credit": 1.5},
{"code": "CSE-305", "name": "Unix Programming", "Credit": 3.0}]
# Print the sorted dictionary based on code
print("Sorting based on the code:\n", sorted(dic_list, key=lambda i: i['code']))
# Print the sorted dictionary based on name
print("Sorting based on the name:\n", sorted(dic_list, key=lambda i: (i['name'])))
# Print the sorted dictionary based on code and name
print("Sorting based on the code and name:\n", sorted(dic_list, key=lambda i: (i['code'], i['name'])))
# Print the sorted dictionary in descending based on name
print("Sorting in descending order based on the name:\n", sorted(dic_list, key=lambda i: i['name'], reverse=True))
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script.
Conclusion:
The uses of lambda for sorting four different lists have shown in this tutorial by using simple examples that will help the python users to understand the purpose of using lambda in sorting.