In my daily workflow, I work with many remote Linux systems, most of which are Debian-based.
I can openly tell you that sometimes, it gets very tiresome to SSH into all the machines, do an apt-get update, and then check if there are any updates and install them. Even with Password-Less SSH logins, it still takes an immense amount of time.
After constantly asking myself, “how can I automate this process?” I found Ansible!
For this tutorial, I will show you how to utilize this powerful automation tool to update all your remote systems using apt. Staying up to date and applying all the patches to your system will help keep your system secure.
What is Ansible?
Ansible is a powerful automation tool that allows you to remotely and automatically configure and manage systems. Additionally, it offers compelling features such as installing software remotely, rollbacks in case of errors, backups, remote downloads, and many more.
Ansible is also very easy to use. It utilizes YAML files which are easy to write and highly readable, and a high level of security as it uses SSH to login and manage systems.
Managing more than one system from a single tool is more than triumphant, and any system administrator should be familiar if not already using Ansible.
Installing Ansible
With Ansible’s praises out of the way, let us look at installing Ansible on our local machine to manage the remote servers.
For this tutorial, I will be using Ubuntu 20.10 as my local machine. To learn how to install Ansible on other systems, check out the documentation.
On Ubuntu, use the commands:
sudo apt install software-properties-common
sudo add-apt-repository --yes --update ppa:ansible/ansible
sudo apt install ansible
Ansible Add Hosts
If you are not familiar with Ansible, the first step is to build an inventory of the remote machines you want to automate. You can do this by editing the /etc/ansible/hosts.
To add the Debian servers, enter the entries as:
192.168.0.13
You can pass the IP address of the remote host or use the hostname of the machine.
Once we have the list of hosts to manage in the config file, we can proceed and automate the updates.
Update Using The apt Module
To update and manage packages remotely on Debian-based machines, we use the apt module provided by Ansible. The apt module allows us to manage apt packages with other configurations.
Update Repository Cache
To update the repository cache using Ansible, we can use a playbook as provided below:
- hosts: debian
become: yes
become_method: sudo
tasks:
- name: "Update Repository cache"
apt:
update_cache: true
cache_valid_time: 3600
force_apt_get: true
Save the file and run using the command as:
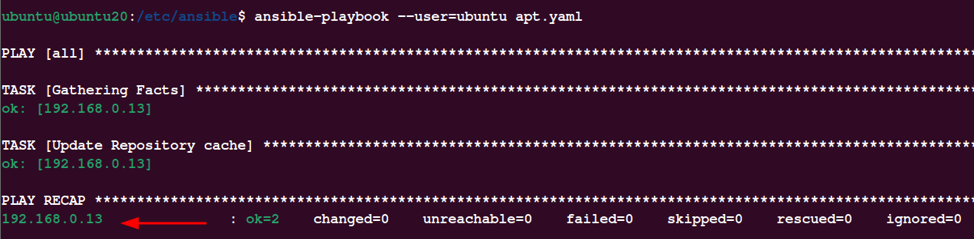
This will run the playbook and execute the tasks specified. The output is as shown below:
In the Ansible playbook, we start by specifying the hosts. In this case, we only want the Debian hosts.
Next, we set it to become true, allowing the user to elevate privileges using sudo as specified in the becom_method.
Finally, we set the tasks to update the repository cache. We also set a cache_valid_time as 3600 that refreshes the cache if it is older than said time.
NOTE: Use force_apt-get instead of aptitude.
Upgrade all packages
We also can update all the packages in the system which corresponds to the command:
To do this using Ansible playbook, we add the yaml file as:
- hosts: all
become: yes
become_method: sudo
tasks:
- name: "Update cache & Full system update"
apt:
update_cache: true
upgrade: dist
cache_valid_time: 3600
force_apt_get: true
Similarly, run the Ansible Playbook above, as shown in the first command.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we quickly went over what Ansible is, what it offers, and how we can use its modules to perform a system update on Debian based system.
Thank you & Happy Automation