Prerequisites:
Before starting the steps of this tutorial, the following steps will be required to complete.
Enable the SSH service on Ubuntu if it is not enabled before.
Generate the SSH Key pairs to execute the commands in the remote server. Run the following command to create the public key and the private key. The private key will be stored in the remote server, and the public keys will be stored in the client securely.
Run the following command to open the sshd_config file using nano editor to add some necessary configurations.
Add the following lines in the file to enable the root login and password-based authentication.
PermitRootLogin yes
Run the following command to restart the SSH service.
Run the different types of SSH Commands:
You can check the tasks of the SSH commands by using the remote server or the local server. Two user accounts of Ubuntu have been used here to run the SSH commands in the local server. One user account has been used as a client, and another user account has been used as a server in this tutorial to check the way of executing the command in the server machine from the client machine using SSH.
Run the single command:
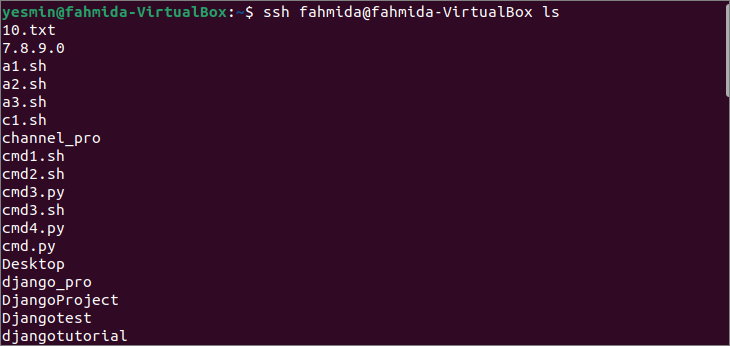
Run the following command to execute the `ls` command in the remote host using the hostname. Here, ‘yesmin@fahmida-VirtualBox’ has worked as a client machine, and ‘fahmida@fahmida-VirtualBox’ has worked as a server machine.
The following output shows the list of all files and folders of the current directory of the remote host. Here, the username of the remote host is ‘fahmida.’
Run the following command to execute the `pwd` command in the remote host by using the IP address of the remote host. Here, ‘yesmin@fahmida-VirtualBox’ has worked as a client machine, and ‘[email protected]’ has worked as a server machine.
The following output shows the path of the current working directory of the remote host where the username of the remote host is ‘fahmida.’
Run multiple commands:
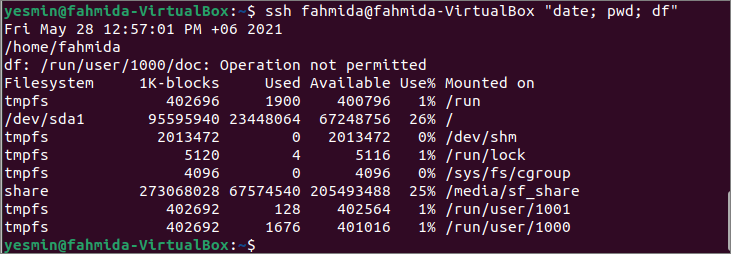
Run the following command to execute three commands, `date,` `pwd,` and `df,` using a single SSH command in the remote host by using the hostname. Here, ‘yesmin@fahmida-VirtualBox’ has worked as a client machine, and ‘[email protected]’ has worked as a server machine.
The following output shows the output of the three commands after executing in the remote host where the username of the remote host is ‘fahmida.’
Run multiple commands with pipe:
Create a text file named fruits.txt with the following content in the remote host used in the next SSH command.
fruits.txt
Mango
Banana
Watermelon
Guava
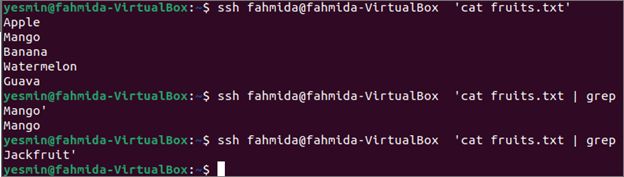
Run the following SSH command from the client’s terminal to check the content of the fruits.txt file that exists in the server.
Run the following SSH command from the client’s terminal to check the word ‘Mango’ exists or not in the fruits.txt file.
Run the following SSH command from the client’s terminal to check the word ‘Jackfruit’ exists or not in the fruits.txt file.
The following output will appear after executing the above three SSH commands. The following output shows that ‘Mango’ exists in the file and ‘Jackfruit’ does not exist.
Run command to execute the script:
Executing any bash script of the remote host using the SSH command has been shown in this part of the tutorial. Create a bash file named read.sh with the following script in the remote host. The script will take an input value from the user and print the input value by combining it with the other string after execution.
read.sh
read -p "Do you like Mango? " ans
answer=${ans^^}
echo "Wow! You like $answer."
Run the following SSH command to check the content of the read.sh file that is located in the remote host.
The following output will appear if the file exists in the remote host.
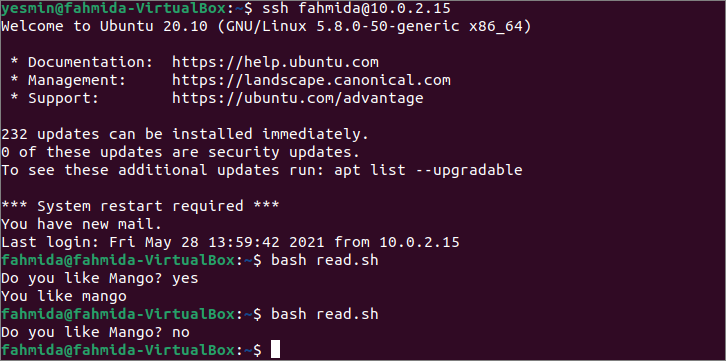
Run the following SSH command to connect with the remote host using the IP address.
Run the following command to execute read.sh file after login to the remote host.
The following output will appear after executing the above commands. The bash file has been executed two times here with two different values.
Run `sudo` command:
Executing the `sudo` command after logging into the remote host using the SSH command has been shown in this part of the tutorial.
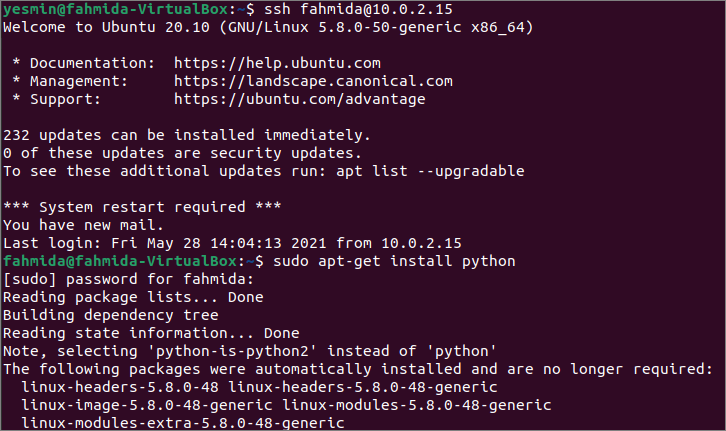
Run the following SSH command to log in to the remote host using the IP address of the remote host.
Run the following command to install the Python in the remote host after the successful login. It will ask for the password of the username of the remote host to start the installation process.
The following output will appear after executing the above commands.
Terminate from the SSH:
Run the following command to terminate the connection from the remote host.
Conclusion:
The ways to execute single and multiple commands, the commands with pipe, the command to run a particular bash file, and the use of the `sudo` command in the remote host have been shown in this tutorial. The reader will run the SSH command in the remote host after reading this tutorial properly.