Working of Pthread Priority In Operating System:
A thread ID distinctively recognizes each thread. When threads are formed, they initiate to pass parameters while executing a function. A thread can pause for another thread to execute and return a value. Threads execute one by one. You can also set the priority attribute before creating a thread.
Install Prerequisites:
So, the Pthread priority attribute needs some libraries to be installed to work on it. If somebody wants to use threads in their code, they have to use the built-in library of C language Pthread, allowing the pthread to work in the code.
Another prerequisite required to compile the code having Pthread in it is the GCC compiler. This is because we are using the Pthread. So, to execute and compile C language code, we must have some compiler package installed in our system. So, here we have to install the GCC compiler. You can install it using the very simple Sudo apt command at your Linux terminal as below. It will complete its installation in a few minutes, and you can easily write C codes in files and execute them.
By pressing the enter key, it will start installing gcc compiler in your Ubuntu server. It will take few moments; then it will ask you to enter yes/No; at that time, you have to enter yes, then it will start screening the progress of gcc compiler downloading as shown in the image below:
Example of Pthread Priority in C Language:
Let’s start working on Pthread to understand it well. First of all, you have to create a C-type file using the text editor in the command-line shell. For this, try to run the below simple command in the shell.
The above-shown command will take some time to open, after which you will be able to use it instantly. It directly opens the text editor of your Ubuntu 20.04. The text editor will open up like the image given below:
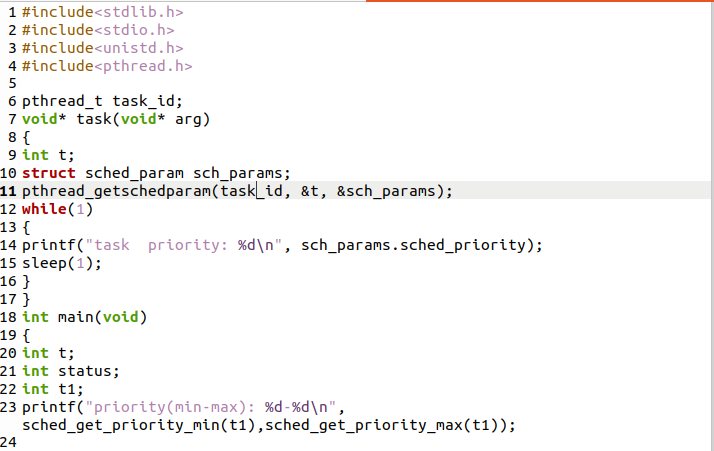
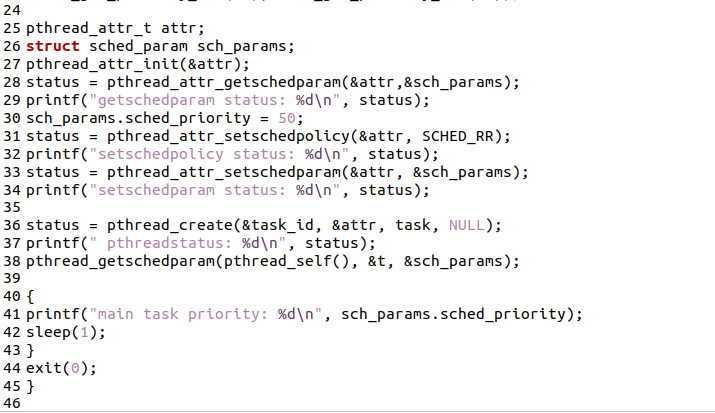
After the file has been created and opened, it’s time to write some C code. So, you can see the below long code in the text editor. The first 4 lines have header files that are necessary to be included in the editor file for the proper working of the pthread. After these header files, we have defined the void function as no parameters. Then we define integers and write a statement to be displayed on the screen, and between these two statements, sleep, a function is used. After that, we have the main class of the program. In the space of the main function, we have declared integers and give priority to the priority min-max statement. After that, we have also declared the pthread built-in function and thread names as shown in code, which will be used in further lines. In the next lines, we are creating multiple threads with different names and processes. In the last line of the code, we use exit() to stop the execution of a loop. More you can understand through code.
Before closing, save the editor text file by using Ctrl+S. Save this above image code with any name using extension as.c. This extension shows that it’s a C language code, and it allows you to show the functions and library of the C language, as shown below.
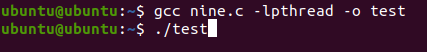
Now you have to compile the above-presented code. For the compilation of code, we have to use the gcc compiler. So, execute the below gcc query to compile the “code.c” file. Move back to the terminal and give the appended command:
As we are using pthread in our code. For this purpose, while executing, you have to use the –lpthread command to operate pthread functions. Now, we have to execute this code using the simple./test command in the shell as below. This command will simply execute the code and return nothing, but the data has been written to a disk drive in the back of the process.
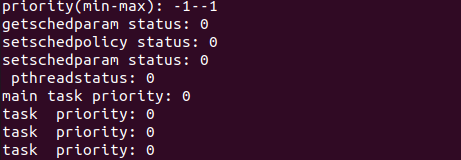
After giving this command to your Ubuntu terminal, it will allow the execution of code. The output of the above-shown code will be showed on your screen. The below affixed is the output of the above-presented code.
This shows the created threads are functioning properly; otherwise, it returns 0. This also shows that priority is given to the priority thread. While multithreading, statements are stored in different threads. Both the threads run differently but showing as they are working parallel.
Conclusion:
We have concisely discussed a very simple and linear example of the pthread priority working in Ubuntu in C language to understand its concept. I hope now you can easily use pthread priority in your code to compile at your Ubuntu 20.04.